Figure 1.
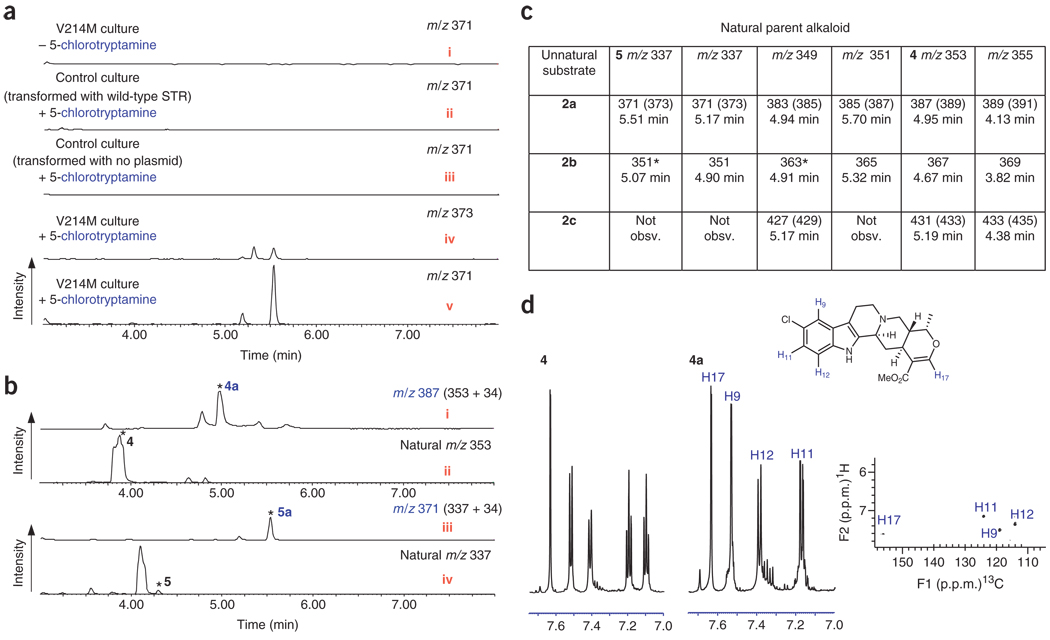
Unnatural alkaloid production in C. roseus hairy root culture expressing reengineered strictosidine synthase V214M. (a) Extracted LC-MS traces for a representative unnatural alkaloid (m/z 337+34) derived from 2a. This compound is not observed when 2a is absent from the medium (i), or in control hairy root cultures transformed with wild-type strictosidine synthase gene (ii), or in control cultures transformed with no plasmid (iii). The compound displays the isotopic distribution expected for a chlorinated compound (iv,v). (b) LC-MS traces showing production of two unnatural alkaloids derived from 2a (i,iii), along with the traces showing production of the parent natural alkaloids from the same cultures (ii, iv). Asterisked compounds 4a (i), 4 (ii) and 5a (iii) were isolated and characterized by NMR. Asterisked compound 5 (iv) was assigned based on coelution with an authentic standard (Bestchemistry, Zhjiang, China). LC-MS spectra of i and ii are normalized to the same y axis scale to allow comparison of the relative amounts of 4 and 4a; iii and iv are normalized to allow comparison of the relative amounts of 5 and 5a. See Supplementary Figure 1 for isotopic peaks associated with chlorinated and brominated compounds. MS data of the additional peaks in trace i suggest that these compounds are chlorinated isomers of 4a (See Supplementary Fig. 1). (c) Tabulated MS data of the major unnatural alkaloids produced from transgenic hairy root lines and 2a, 2b and 2c. Asterisked masses indicate that compounds with identical mass and retention time are present in low amounts in the wild-type control cocultured with tryptamine analog. Asterisked compounds therefore cannot be definitively assigned as unnatural compounds. See Supplementary Figure 1 for MS traces and Supplementary Table 1 for exact mass data. (d) Aromatic region of 1H NMR spectrum of 4 and 1H NMR and 1H-13C HSQC spectra of 4a isolated from transgenic C. roseus hairy root culture expressing V214M cultured with 500 µM 2a.