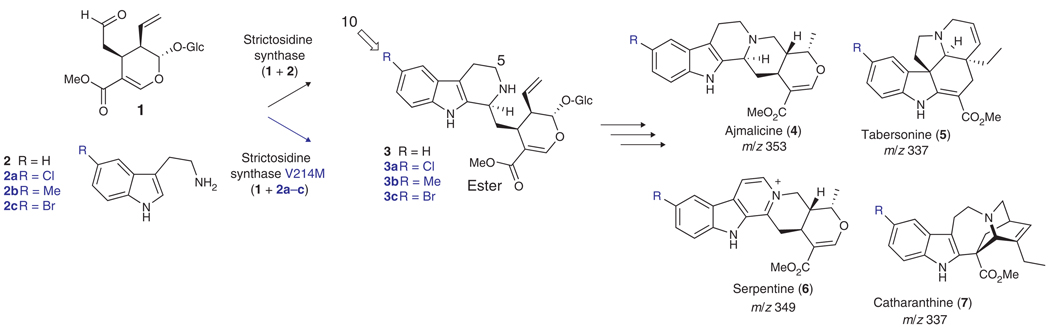
Scheme 1.
Biosynthesis of monoterpene indole alkaloids. Secologanin (1), a complex terpenoid derived from geraniol, and tryptamine (2) form monoterpene indole alkaloids 4, 5, 6 and 7 via the biosynthetic intermediate strictosidine (3). Strictosidine synthase, the enzyme that catalyzes formation of strictosidine, has expanded substrate specificity enabling turnover of tryptamine analogs 2a, 2b and 2c when the point mutation V214M is incorporated into the protein sequence.