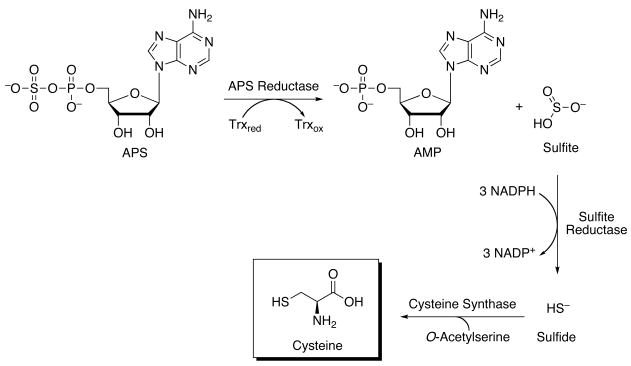
Figure 1.
Sulfate assimilation pathway in M. tuberculosis. The majority of sulfate reducing bacteria use APS as their source of sulfite. In this reaction, APS is reduced to sulfite and adenosine-5′-monophosphate (AMP) by APS reductase. Sulfite, in turn, is reduced by later enzymes in this metabolic pathway, forming first sulfide before incorporation into cysteine and, ultimately, to methionine and other essential reduced sulfur-containing biomolecules.