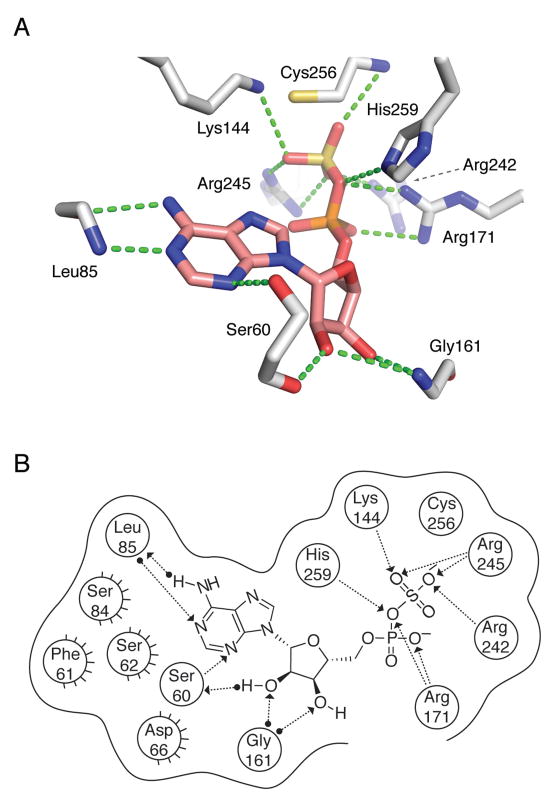
Figure 8.
APS reductase interactions with substrate, APS inferred from P. aeruginosa APS reductase (PDB deposition 2GOY) and S. cerevisiae PAPS reductase (PDB deposition 2OQ2) structures and functional data obtained in the present study. (A) Summary of proposed active site contacts to APS. (B) Summary of proposed active site contacts to APS, plotted in two dimensions. A total of nine protein residues are shown in proximity around the ligand, with hydrogen bonding interactions shown where detected. Hydrogen bonds are draw as dotted lines with arrows denoting the direction of the bond. Interactions from substrate or the residue backbones of the enzyme are distinguished from the interactions with residue side chains by a solid dot at the end of the interaction line. Active site residues between P. aeruginosa and M. tuberculosis APS reductase are largely conserved, with the exception of residues implicated in hydrophobic interactions (Ser62 to Met67, Ser84 to Phe87, Phe61 to Asn66). The corresponding numbers for residues conserved between M. tuberculosis and P. aeruginosa APS reductase are: Ser65 (Ser60), Leu88 (Leu85), Lys145 (Lys144), Gly162 (Gly161), Arg171 (Arg171), Arg237 (Arg242), Arg240 (Arg245) Cys249 (Cys256), and His252 (His259). See also Figure S1.