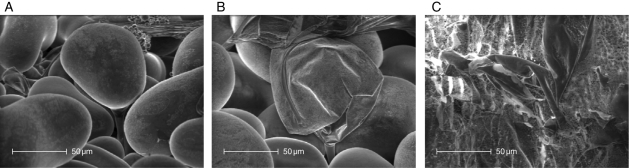
Fig. 5.
Scanning electron micrography of the leaf surface of Atriplex halimus showing bladders (A) consisting of vesiculated balloon-like hairs attached to a stalk and playing a significant role in removing salt from the reminder of the leaf thus preventing accumulation of toxic salts in the parenchyma and vascular tissues. Accumulation of electrolytes leads to the bladder shrinking (B) and then bursting, depositing crystals at the leaf surface (C).