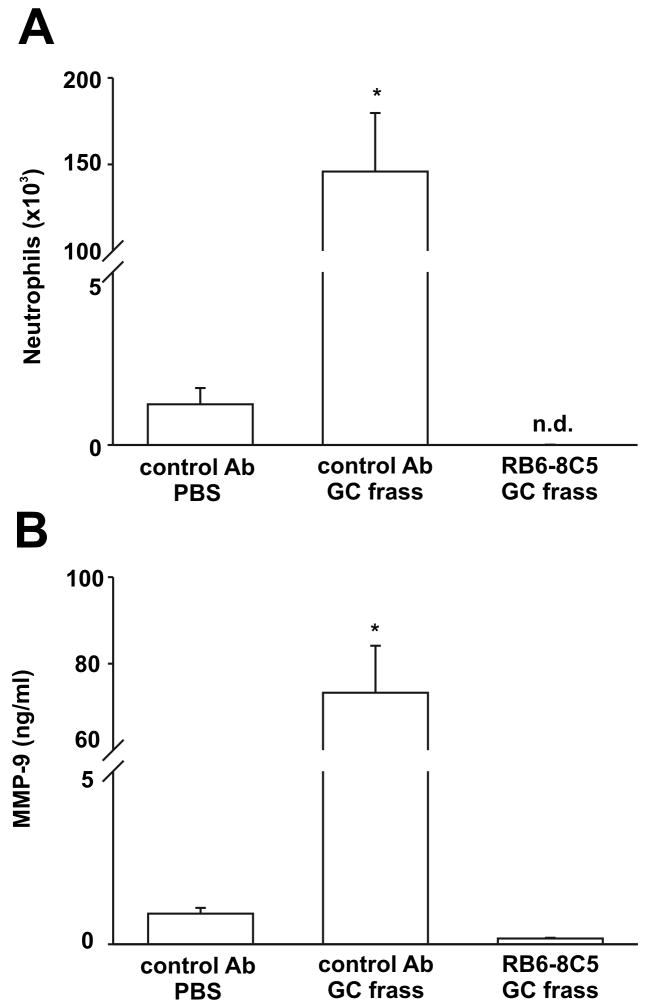
Figure 2.
Neutrophil recruitment directly affected MMP-9 release into the airways. Balb/c mice were given a single injection of control Ab or RB65-8C5 (100 μg/mouse) 24h prior to a single intratracheal inhalation of PBS (40μl) or GC frass (40μg/40μl). 3 h later, mice were given a lethal dose of sodium pentobarbital and BAL fluid was harvested. Neutrophils were quantified following differential staining and a MMP-9 ELISA was performed on the BAL fluid. In all cases, means ± SEM (n=6 mice per group) were reported. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA. A. Neutrophil influx into BAL fluid (*p<0.001) (nd=none detected). B. MMP-9 ELISA of BAL fluid (*p<0.001).