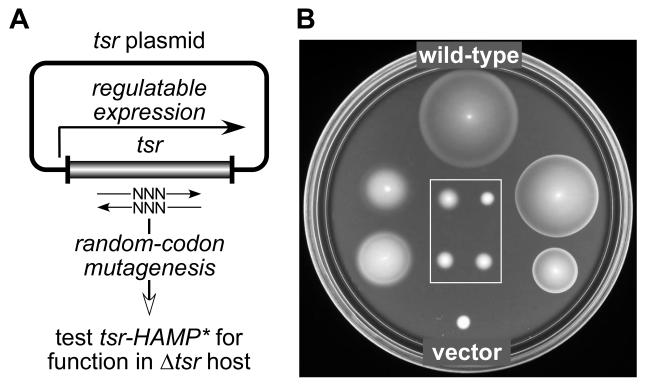
Fig. 2. Isolation of Tsr-HAMP mutants.
A) Strategy for constructing mutations. Mutations were created by randomizing the sequences of individual HAMP codons in plasmids carrying the tsr coding region under inducible expression control. Candidate plasmids were tested for Tsr function in UU1250, a receptorless host that lacks tsr and other MCP family receptors.
B) Examples of mutant Tsr-HAMP phenotypes. UU1250 transformants from (A) were tested for Tsr function on tryptone soft agar plates containing 12.5 μg/ml chloramphenicol and 0.6 μM sodium salicylate and incubated at 30°C for 7 hours. The wild-type control was pPA114; the vector control was pKG116. Eight mutant examples are shown: The two on the left (I229Y, M249S) and the two on the right (I226M, S255E) exhibit reduced or impaired Tsr function (i.e., Tsr±). The four boxed mutants have null defects (i.e., Tsr−).