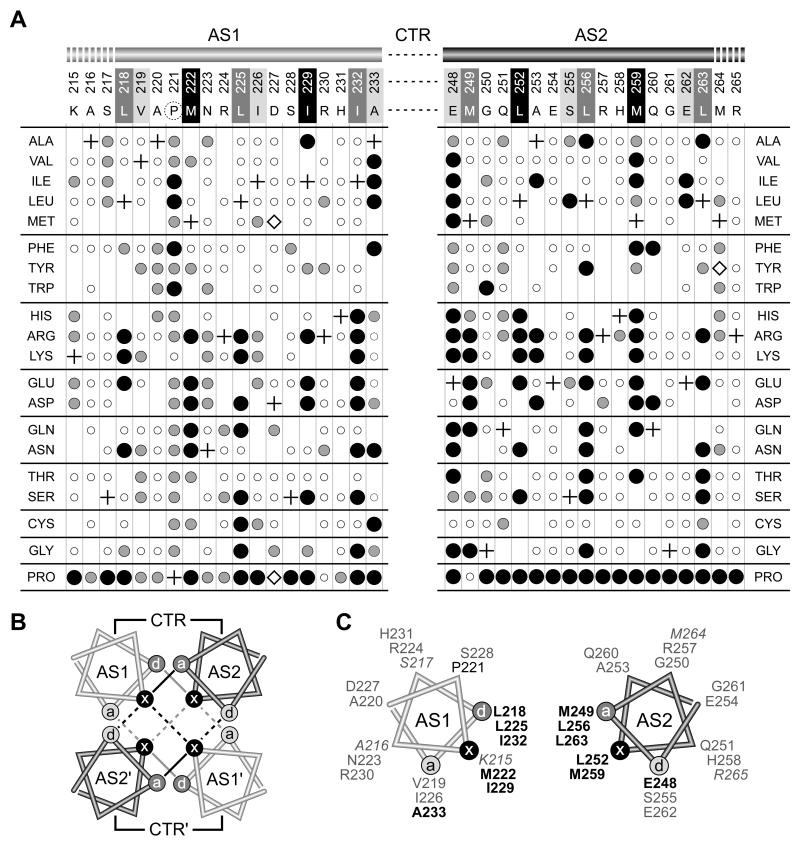
Fig. 3. Mutant phenotypes and packing faces of AS1 and AS2 helices in Tsr HAMP.
A) AS1 and AS2 missense mutants. Residue numbers and wild-type amino acids of Tsr HAMP are shown at the top of the figure. In the x-da packing notation, critical d positions in AS1 and critical a positions in AS2 are shaded dark gray. Noncritical a positions in AS1 and noncritical d positions in AS2 are shaded light gray. Residues at x positions in both helices are shaded black. The dashed circle around P221 indicates that this residue is less critical, but also important for function. Missense changes obtained at each residue are indicated by circles below the corresponding wild-type residue: small, open circles = Tsr+; intermediate-sized gray circles = Tsr±; large black circles = Tsr−. Plus symbols identify the wild-type residues at each position. Where no symbol is given, that particular replacement was not isolated. Mutants denoted by open diamonds expressed Tsr at less than 25% of the wild-type level; all other mutants expressed Tsr at 50% or more of the wild-type level (Table S1).
B) Helix packing in the x-da 4-helix HAMP bundle. Helical wheels, viewed toward the C-terminus from the N-terminal side, show the x, d, and a positions of the bundle-stabilizing residues (Hulko et al., 2006). Two layers of hydrophobic packing interactions are indicated by black (upper layer) and gray (lower layer) lines. Interactions that stabilize the intrasubunit interface are indicated by solid lines; interactions that stabilize the intersubunit interface are indicated by dashed lines.
C) One subunit of the x-da bundle. The AS1 and AS2 residues important or critical (bold) for function are labeled in black type; noncritical residues are labeled in gray type. Italic labels indicate residues on the N-terminal (K215-S217) or C-terminal (M264-R265) side of the HAMP bundle that may serve as transmission links to adjacent domains (see Discussion).