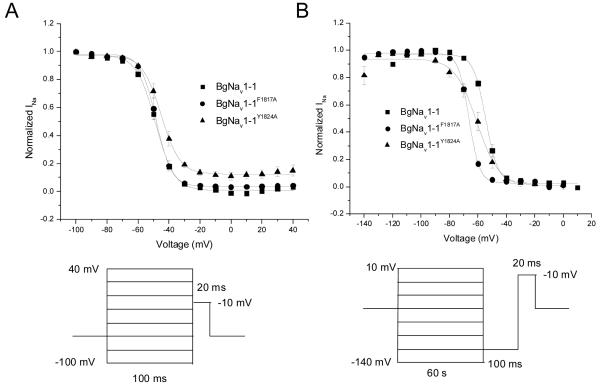
Figure 2.
Effect of alanine substitutions of F1817 and Y1824 in IVS6 on the voltage-dependence of fast (A) and slow (B) inactivation of BgNav1-1a channels. Fast inactivation was measured with 200-ms conditioning pulses to potentials ranging from -100 to 40 mV from a holding potential of -60 mV (BgNav1-1a and BgNav1-1aY1824A) or -65 mV (BgNav1-1aF1817A) followed immediately by 20-ms test pulses to -10 mV. Slow inactivation was measured using 60-s conditioning pulses to potentials ranging from -140 to 10 mV followed by hyperpolarizing pulses to -120 mV (100 ms) to remove any fast inactivation and 20-ms test pulses to -10 mV. Conditioning and test pulses were applied from holding potentials of -60 mV (BgNav1-1a and BgNa 1-1aY1824A) or -65 mV (BgNav1-1aF1817A v). Currents were normalized to the amplitude of the largest recorded current.