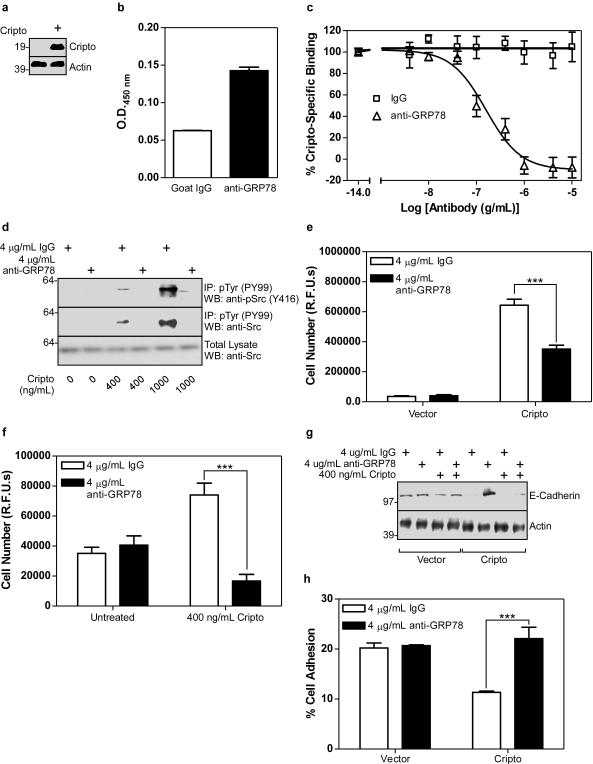
Figure 4. Cripto binding to cell surface GRP78 mediates oncogenic Cripto effects in human mammary epithelial cells.
(a) Cell lysates from control or Cripto-infected MCF10A cells were analyzed by Western blot using Cripto and actin antibodies as indicated. Human mammary epithelial MCF10A cells infected with empty vector were subjected to intact cell ELISA using IgG or anti-GRP78 (b) or to 125I-Cripto binding in the presence of a range of doses of anti-GRP78 or control IgG antibody as indicated (c). (d) MCF10A cells infected with empty vector were serum starved and then treated with the indicated doses of soluble Cripto, anti-GRP78 and/or IgG as indicated. Resulting cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-phospho-Tyr (pTyr) antibody and Western blotting with anti-phospho-Src (pSrc, Y416) or anti-Src antibodies as indicated. MCF10A cells infected with either empty vector or Cripto (e) or with empty vector (f) were treated with soluble Cripto, IgG and/or anti-GRP78 as indicated. Cells were grown for 8 days and proliferation was measured using the CyQuant proliferation assay kit. (g) MCF10A cells infected with empty vector or Cripto were treated with soluble Cripto after pretreatment with IgG or anti-GRP78 as indicated. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot using E-Cadherin and actin antibodies. (h) MCF10A cells infected with empty vector or Cripto were pretreated with IgG or anti-GRP78, plated and allowed to adhere. Resulting cell adhesion was quantified using the CyQuant adhesion assay. ***p<0.001.