Figure 3.
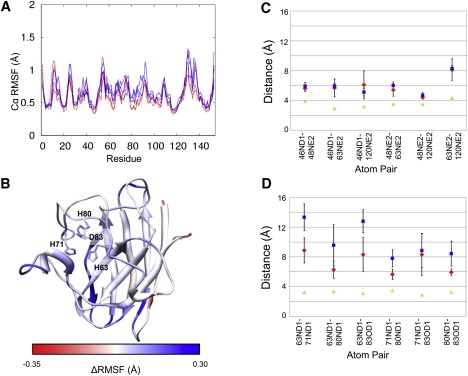
Changes to metal-binding residues. (A) Cα-RMSF by residue for three each WT (light gray, shown in red online) and A4V (dark gray, blue online) simulation. (B) Differences in Cα-RMSF are mapped onto the protein structure. Regions with a higher RMSF in the mutant than in the WT are shown in dark gray (blue online), and regions with higher RMSF in the WT than in the mutant are shown in light gray (red online). White indicates no difference. The four residues displayed are the Zn2+-binding residues. H71, H80, and D83 each show higher RMSF and RMSD (not shown) in the A4V mutant simulations than in the WT. (C) Average pairwise distances between the Cu2+-binding atoms for three simulations of WT (diamonds) and A4V (squares) proteins. In each case the error bars represent the SD of the three simulations, and in each case the error bars overlap. The WT crystal structure distances are shown as triangles. Mutant crystal structure distances differ from WT by <0.2 Å in all cases, including those shown in panel D (not shown). (D) Average pairwise distances between the Zn2+-binding atoms for three simulations of WT (diamonds) and A4V (squares) proteins. In each case the error bars represent the SD of the three simulations. There are significant differences between the distances of the pairs: 63ND1-71ND1, 63ND1-83OD1, 71ND1-80ND1, and 80ND1-83OD1. Triangles are as in panel C.
