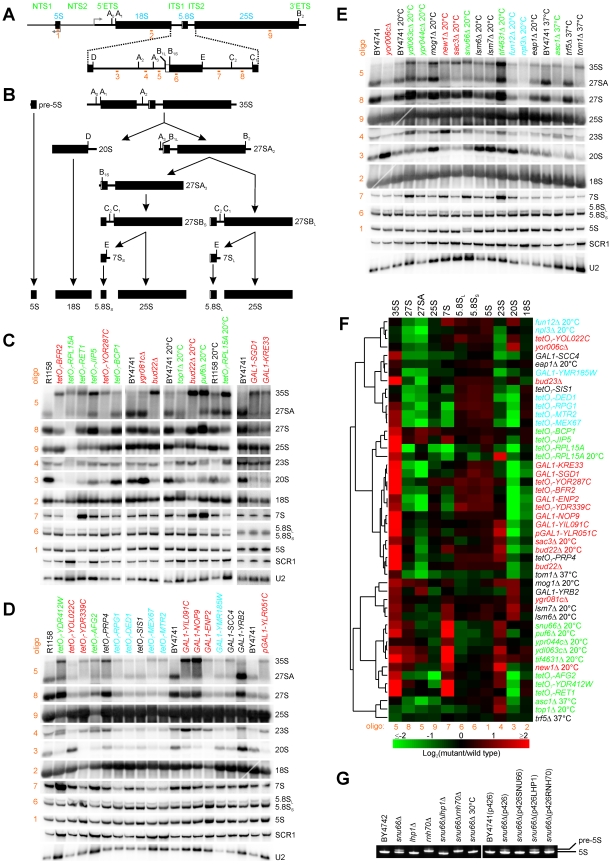
Figure 5. Characterization of mutant pre-rRNA and rRNA processing defects using quantitative Northern blots.
(A) Oligonucleotide probes (orange numbers; see Table S2 for sequence information) within an rDNA repeat were selected to probe the majority of pre-rRNA and rRNA species generated during the pre-rRNA processing pathway, diagrammed in (B). Precise processing defects associated with each mutant strain were identified by Northern blots (C–E) of different pre-rRNA and rRNA species in wild-type and mutants. Strain label colors are the same as in Figure 2. (F) Global trends among the mutant strains could be observed from hierarchical clustering of mutant strains on the basis of pre-rRNA and rRNA abundances measured from the Northern blots (C–E), with red and green colors representing increased and decreased levels of RNA species, respectively, in mutants relative to corresponding wild-type control strains. The defect of the SNU66Δ strain was examined in more detail in (G). In particular, the temperature-dependent 5S processing defect of this strain could be rescued by deletion of LHP1. 5S rRNA was assayed by 10% TBE-Urea gel and SYBR Gold staining. BY4742 is the wild-type control strain for deletion strains, and BY4741(p426) is the wild-type control strain for over-expression strains. Strains were cultured at 20°C unless otherwise indicated.