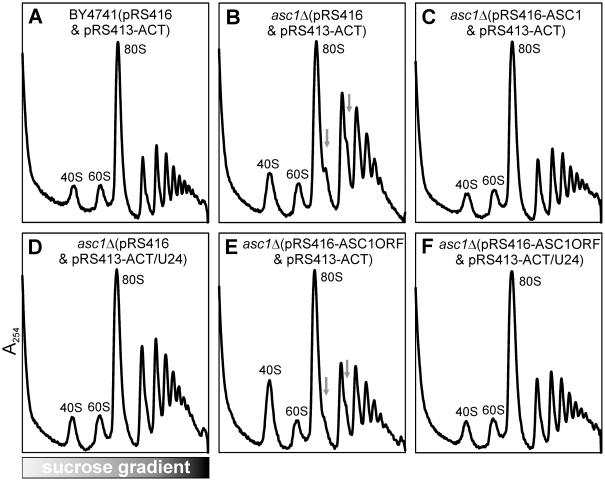
Figure 6. The U24 snoRNA is responsible for the 60S biogenesis defect observed in an asc1Δ mutant.
Polysome profile of wild-type strain with two control plasmids was shown in (A). The asc1Δ mutant with two control plasmids showed the 60S biogenesis defect (B), and this defect was recovered by full length intron-containing ASC1 gene (C) or intron snoRNA U24 of ASC1 (D), but not by the coded protein of ASC1, deleted of its intron (E). When the intron snoRNA U24 of ASC1 was put back into the asc1Δ mutant expressing the coded protein of ASC1, the polysome profile recovered to wild-type (F). All strains were cultured at 37°C. pRS416 and pRS413-ACT are the control plasmids; pRS416-ASC1 carries full length ASC1 with both intron and exon; pRS413-ACT/U24 carries the intron sequence of ASC1; and pRS416-ASC1ORF carries the sequence of protein coding region of ASC1. Peaks corresponding to 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits and 80S mono-ribosomes in the polysome profiles were labeled. Gray arrows indicate the halfmer polysomes.