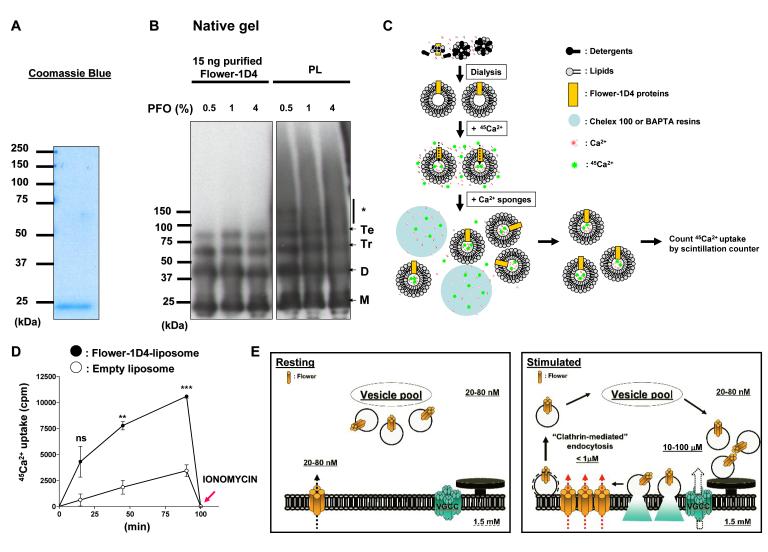
Figure 7. Flower can form a Ca2+-permeable cationic channel.
(A) The purified Drosophila Flower-1D4 protein was boiled for 5 min in the presence of 2% SDS and 2.5% β-mercaptoethanol, separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, and stained with Coomassie blue. (B) Purified Flower-1D4 proteins or Flower-containing proteoliposomes (PL) were incubated with 0.5, 1, or 4% perfluoro-octanoic acid (PFO) sample buffers and run on a 4-12% gradient Tris/glycine precast native gel. Multimeric Flower complexes were observed. Monomers (M), dimers (D), trimers (Tr), tetramers (Te), higher oligomers (*). (C and D) Experimental paradigm for the radioactive 45Ca2+ influx assay. Quantification is shown in D. Three independent experiments were used for quantification. P value: ns, not significant; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Error bars indicate SEM. (E) Proposed model. Flower, a SV- and presynaptic membrane-associated Ca2+ channel, fuses with the presynaptic membrane upon exocytosis. It then permits a Ca2+ influx which regulates endocytosis as well as resting intracellular Ca2+ levels. Upon endocytosis the majority of the Flower protein is removed, as is typically observed for SV-associated proteins. The remainder of the protein probably affects the resting Ca2+ levels in the presynaptic terminals.