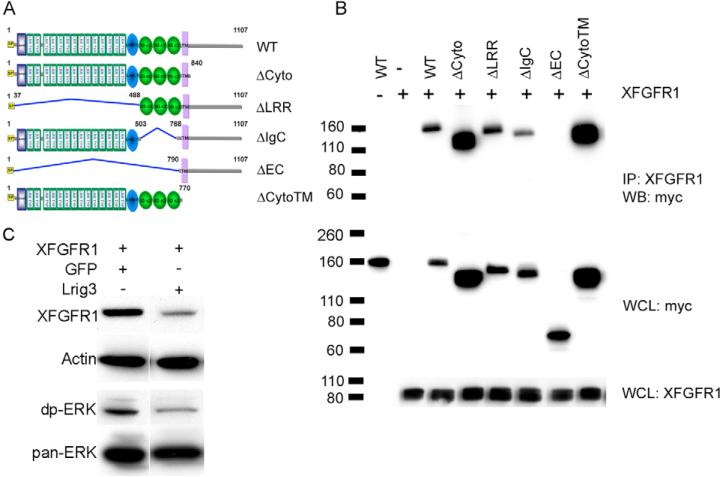
Fig. 7. Lrig3-Xfgfr1 interactions.
(A) The domain structure of wild-type Lrig3 and its deletion mutants; all constructs were tagged with Myc. LRRNT (blue box), leucine-rich repeat N-terminal domain; LRR TYP, leucine-rich repeats, typical; LRRCT (blue oval), leucine-rich repeat C-terminal domain; IG C2 (green oval), immunoglobulin C-2 Type; SP (yellow), signal peptide;. TM (purple), transmembrane domain. (B) Lrig3 binds to Xfgfr1 through its ectodomains. Co-immunoprecipitation was carried out in extracts of 293T cells co-transfected with Xfgfr1 and wild type or mutants of Lrig3 using anti-Xfgfr1 antibody, and blotted with anti-Myc antibody. (C) Lrig3 decreases Xfgfr1 levels. 293T cells were co-transfected with Xfgfr1 and Lrig3 or GFP, which was used to adjust the amount of DNA. Xfgfr1 and endogenous diphospho-ERK and Pan-ERK were detected by western blotting. Actin was employed as a loading control. IP, immunoprecipitate; WCL, whole cell lysate; WB, western blot.