Fig. 1.
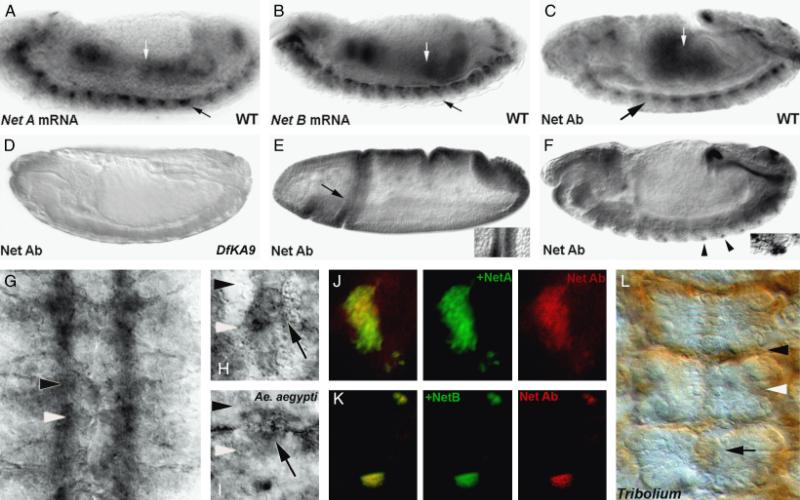
Anti-afrNetrin is a cross-reactive antibody. The anti-afrNet antibody was characterized in Drosophila melanogaster (fly embryos are shown in all panels except I, Aedes aegypti and L, Tribolium castaneum). Net A (A) and Net B (B) mRNA are detected in the gut (white arrows) and CNS (black arrows) of St. 14 D. melanogaster embryos. Expression is detected in these tissues with the cross-reactive anti-afrNet antibody in a slightly older embryo (C). Net protein staining is not detected in Df(1)KA9 homozygous mutant embryos (D) which lack both the NetA and NetB genes. In wild-type Drosophila embryos, the antibody recognizes staining corresponding to NetA (St. 6 cephalic fold staining marked by arrow in E is magnified at right) and NetB (lateral neuron staining marked by arrowheads in F is magnified at right) specific patterns. Furthermore, the antibody can detect ectopic Net protein expression when either NetA (J) or NetB (K) are expressed ectopically in third instar eye disc clones (ectopic expression clones marked by GFP at center, Net staining shown in red at right; overlay shown at left). These data suggest that the Net Ab recognizes Net proteins specifically, and that it can recognize both Drosophila NetA and NetB. The cross-reactive Net Ab recognizes Net protein accumulation on CNS axons (G) and midline glia in wild-type fly embryos (high magnification of single segment of St. 15 embryo is shown in H). A similar staining pattern is observed in the A. aegypti (mosquito) embryo (high magnification of midline glia in a single segment is shown in I). Comparable Net accumulation patterns are also observed in the short-germ beetle T. castaneum (marked by arrow in L; three segments shown). These data indicate that the anti-afrNet antibody is a cross-reactive antibody that specifically recognizes expression of Net proteins in multiple insects, which possess a conserved set of Net-positive midline cells. In this figure, the locations of the anterior commissures are marked with black arrowheads, while posterior commissure locations are marked with white arrowheads. Anterior is oriented left in (A–F) and up in (G–I) and (L).