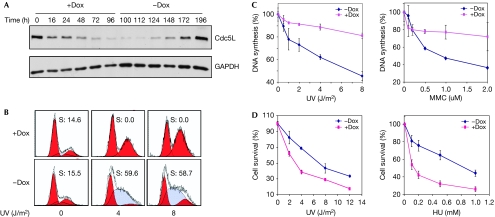
Figure 2.
Depletion of Cdc5L results in a defective S-phase checkpoint and hypersensitivity in response to DNA damage. (A) Dox was added to HCT-116 cells expressing the Cdc5L shRNA for the indicated time periods. At the 100-h time point Dox was removed and cells were kept in fresh medium for the indicated time periods. (B) Cell-cycle profiles of HCT-116 cells with or without the depletion of Cdc5L. Cells were incubated for 48 h with or without Dox, treated with the indicated dose of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and, 16 h later, analysed by FACS for cell-cycle distribution. Numbers inside the panels indicate the percentage of S-phase cells as determined by the ModFit modelling programme. (C) Quantification of DNA-synthesis assays of HCT-116 cells with or without the depletion of Cdc5L and after being exposed to the indicated genotoxic agents. (D) HCT-116 cells were treated with Dox for 48 h and then exposed to the indicated genotoxic agent; cell survival was determined by a clonogenic assay. Cdc5L, cell division cycle 5-like protein; Dox, doxycycline; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HU, hydroxyurea; MMC, mitomycin C; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.