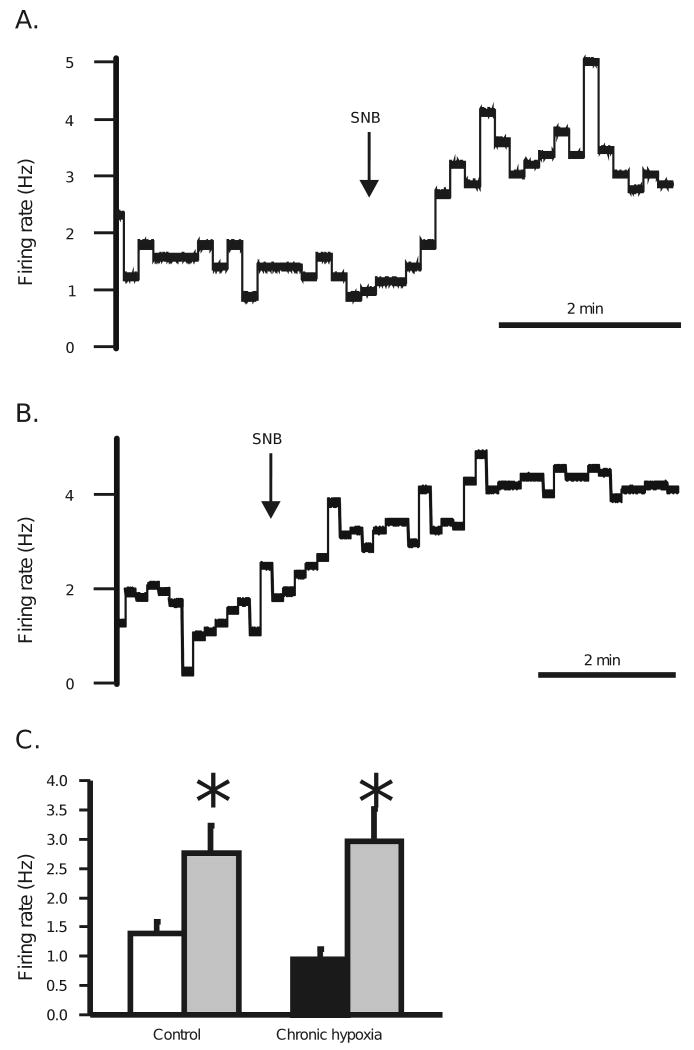
Figure 5.
A: Effect of synaptic blockade medium (SNB—11.4 mM Mg2+ and 0.2 mM Ca2+) on basal firing rate of an SC neuron from a control adult rat. Exposure to SNB solution is denoted by the arrow. Notice that SNB causes an increase in basal firing rate. B: Effect of SNB on basal firing rate of an SC neuron from an adult rat adapted to CHx. Exposure to SNB solution is denoted by the arrow. Notice that SNB causes an increase in basal firing rate. C: The average basal firing rate for SC neurons from control animals (white bar) significantly increases in the presence of SNB (22 neurons from 7 rats) (gray bar) (* indicates P = 0.0035). The average basal firing rate for SC neurons from adult rats adapted to CHx (black bar) also significantly increases in the presence of SNB (22 neurons from 9 rats) (gray bar) (* indicates P = 0.0004). The height of each bar represents the mean firing rate for that group and the error bars represent 1 SEM.