Figure 7.
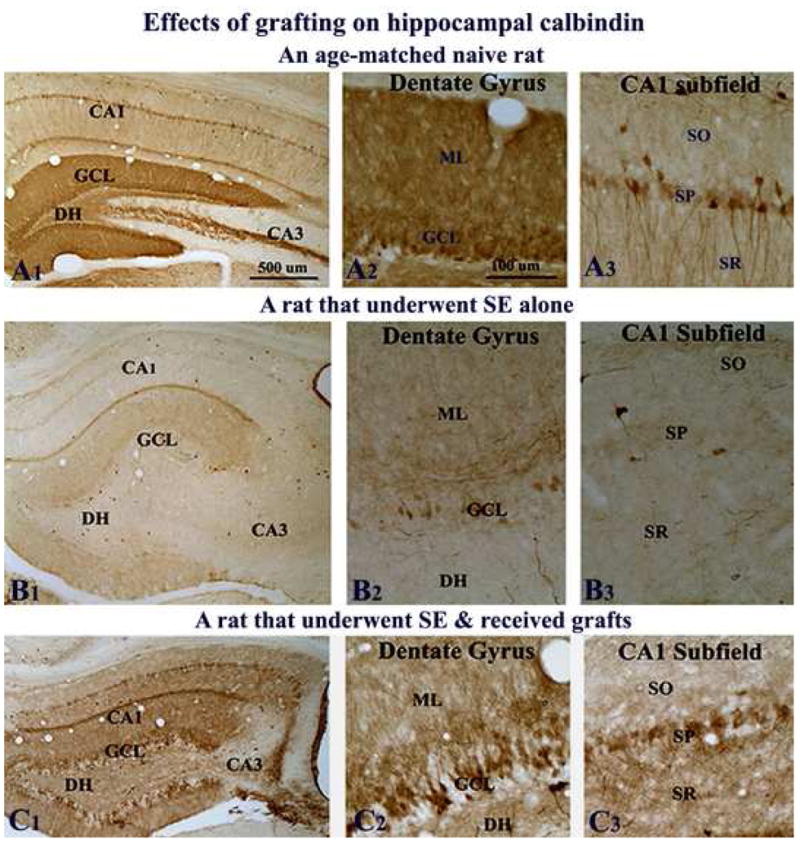
Effects of grafting on calbindin immunoreactivity. Figures show calbindin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of a naive adult rat (A1–A3), a rat that exhibited SE-induced chronic epilepsy (B1–B3), and a rat that underwent SE and received grafts of striatal precursor cells (C1–C3). A2–A3, B2–B3 and C2–C3 are magnified views of dentate and CA1 regions from A1, B1, and C1. Note that calbindin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus diminishes dramatically in both dentate granule cells and CA1 pyramidal neurons during SE-induced chronic epilepsy (B1–B3), in comparison to the naive hippocampus. Contrastingly, when rats that underwent SE receive striatal precursor cell grafts, substantial amount of calbindin is preserved in both dentate gyrus and CA1 subfield of the hippocampus during the chronic phase (C1–C3). Scale bar, A1, B1, C1 = 500μm; A2–A3, B2–B3, C2–C3 = 100μm. DH, dentate hilus; GCL, granule cell layer; ML, molecular layer; SO, stratus oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum.
