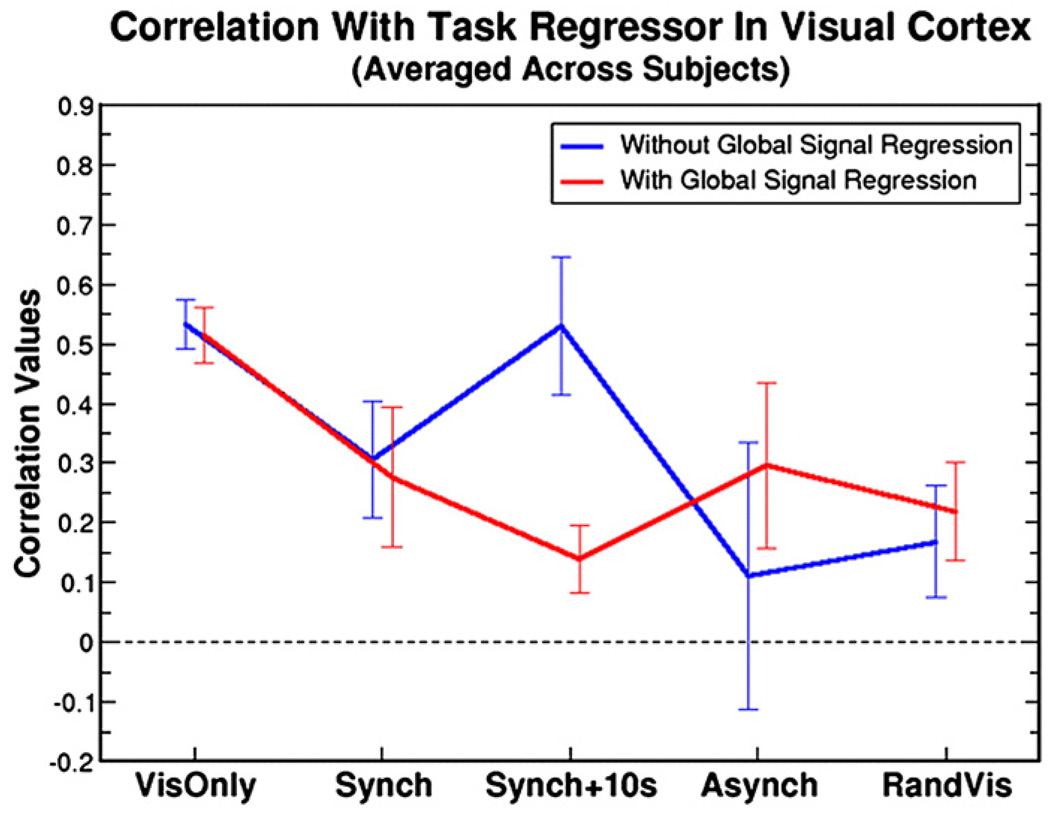
Fig. 3.
Correlation values averaged over the visual cortex and over subjects are shown for the combined breath holding and visual task. Each of the five conditions demonstrate how the relative phase of global (breath hold) and “resting state” (visual) signal changes affects the correlation measure with and without global signal regression (red and blue lines respectively). The significance levels for all comparisons were determined using paired t-tests: VisOnly P = 0.42, Synch P = 0.23, Synch + 10 s P = 8.9×10−6, Asynch P = 7.7×10−4, RandVis P = 0.045. When the phase of the breath hold and visual responses are the same (Synch + 10s condition), global signal regression causes a large reduction in correlation value in the visual cortex.