Abstract
A rapid microradioimmunoassay (RIA) technique was adapted for quantitatively measuring antibody titers to antigens occurring in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected lymphoid cells. In these experiments two EBV-infected cell lines, HR1K and EB-3, were used as antigen-positive cells and Molt-4 was used as the negative control cells. The antibody titers of sera from suspected infectious mononucleosis patients were compared by RIA and indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) methods. As determined by each of the methods, 14 of 19 sera had positive antibody titers and the remainder of the sera had negative antibody titers. Thus, the two methods agreed completely in differentiating sera with antibodies to EBV antigens. To further evaluate the antibody specificity of the RIA, the antibody titers of paired sera, pre- or early infection and postinfection, from five confirmed infectious mononucleosis patients were determined by RIA and IFA. Seroconversion was demonstrated by both RIA and IFA for each of the patients. Thus, the sensitivity and specificity of the two procedures are about the same.
Full text
PDF
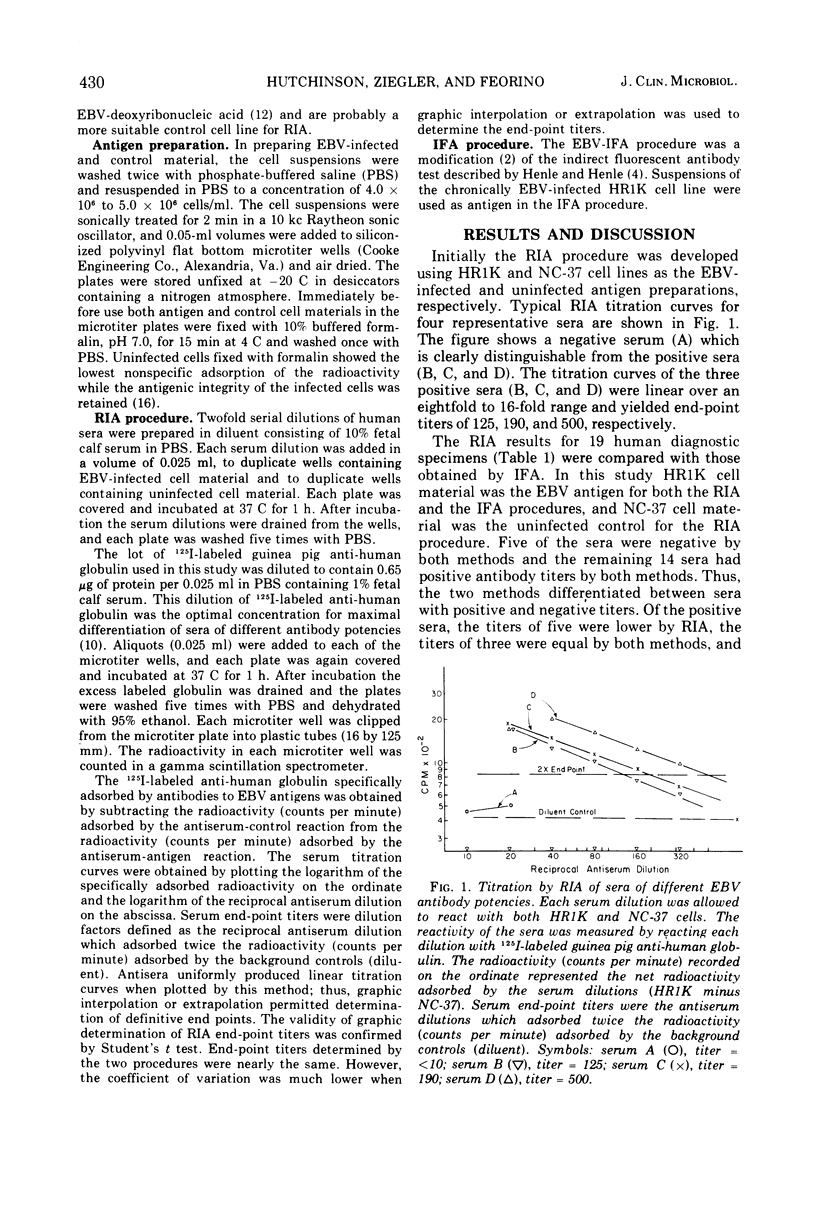
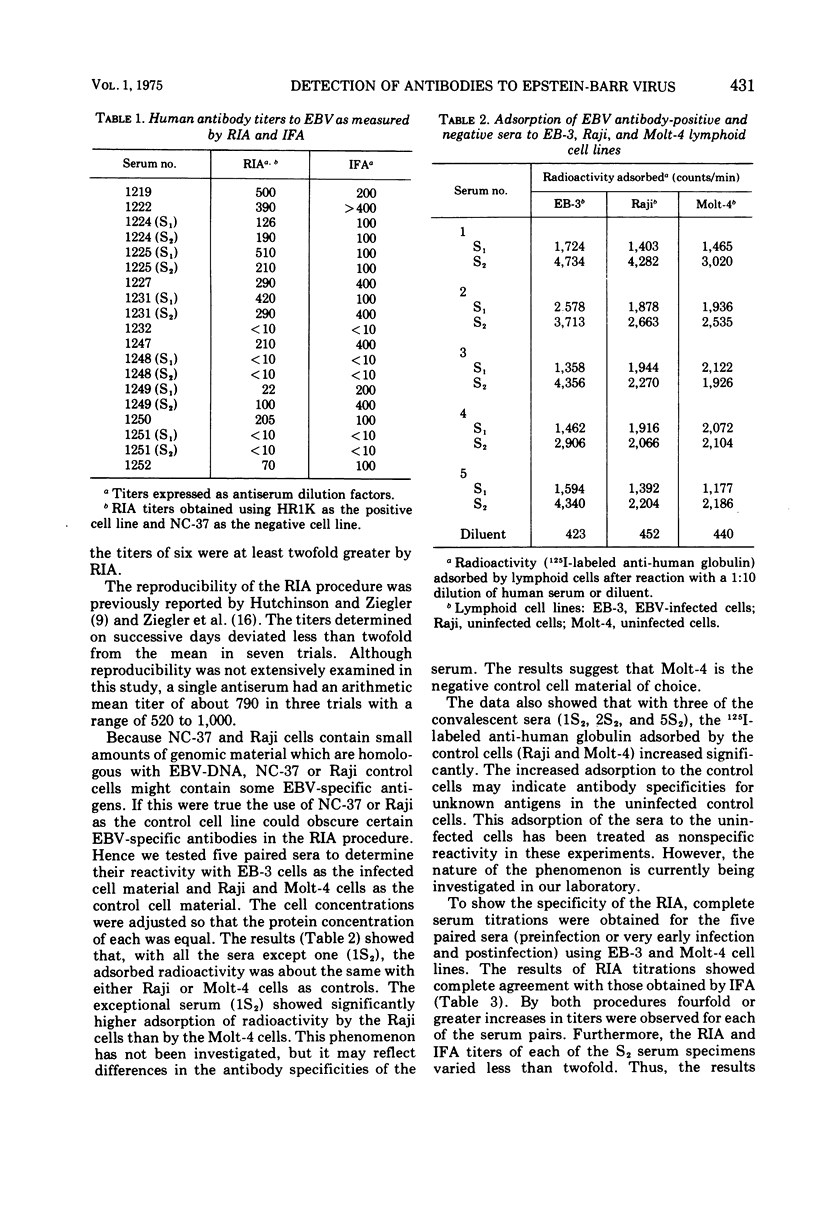


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein M. A., Barr Y. M., Achong B. G. Studies with Burkitt's lymphoma. Wistar Inst Symp Monogr. 1965 Sep;4:69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Dye L. A., Humphrey D. D. Comparison of diagnostic tests for infectious mononucleosis. J Am Coll Health Assoc. 1971 Feb;19(3):190–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewetson J. F., Gothoskar B., Klein G. Radioiodine-labeled antibody test for the detection of membrane antigens associated with Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jan;48(1):87–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Henle G., Henle W. Fine structure of a virus in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1366–1368. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1366-1368.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Criteria for preparing, evaluating, and standardizing iodinated globulins for radioimmunoassay procedures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):935–942. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.935-942.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Simplified radioimmunoassay for diagnostic serology. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.742-749.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Klein G. Reactivity of radioiodinated serum antibody from Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients against culture lines derived from Bukrkitt's lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jul;7(1):39–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Reassociation kinetics for Epstein-Barr virus DNA: nonhomology to mammalian DNA and homology of viral DNA in various diseases. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1006-1012.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Pearson G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Klein E., Henle G., Henle W., Clifford P. Relation between Epstein-Barr viral and cell membrane immunofluorescence of Burkitt tumor cells. I. Dependence of cell membrane immunofluorescence on presence of EB virus. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1011–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genome in nonproductive cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 22;233(38):103–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio233103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. W., Hutchinson H. D., Koplan J. P., Nakano J. H. Detection by radioimmunoassay of antibodies in human smallpox patients and vaccinees. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.311-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hansen H., Diehl V., Wolf H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Schneider U. Occurrence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):189–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio237189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


