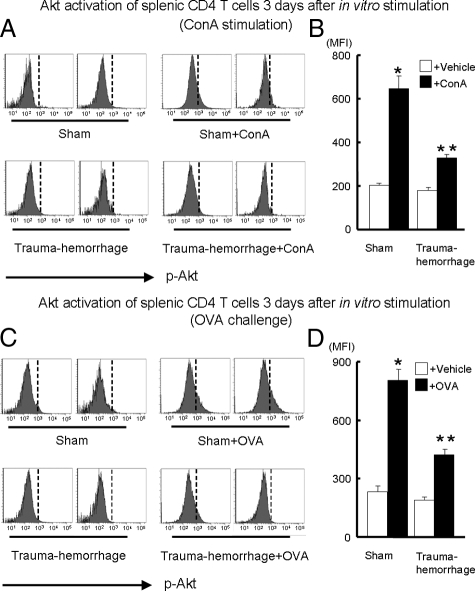
Figure 5.
Expression of p-Akt on cultured splenic CD4+ T cells after in vitro ConA or OVA stimulation. For ConA stimulation, purified CD4+ T cells from sham or trauma-hemorrhage animals were resuspended in complete RPMI 1640 medium with or without 5 μg/ml of ConA and plated in a 96-well plate at a cell density of 1 × 105 cells/well. For OVA stimulation, isolated splenic macrophages from a sham mouse were first incubated for 30 minutes with 50 μg/ml mitomycin C to serve as APCs. After washing, APCs were cultured with CD4+ T cells (1 × 105 cells/well at a 1:1 ratio) purified from OVA-immunized sham or trauma-hemorrhage animals in RPMI 1640 medium with or without 0.1 mg/ml of OVA. After 3 days of culture, cells were harvested and stained with APC anti-CD4 Ab. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-p-Akt Ab as described in Materials and Methods. Representative histograms were gated on CD4+ T cells and showed MFI of p-Akt after ConA stimulation (A) or OVA challenge (C). MFI data for p-Akt after ConA stimulation (B) or OVA challenge (D) are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus all of the other groups. **P < 0.05 versus vehicle groups. n = 5/group. The vertical dotted line in each histogram is intended for better recognition of the shift of MFI among different treatment groups.