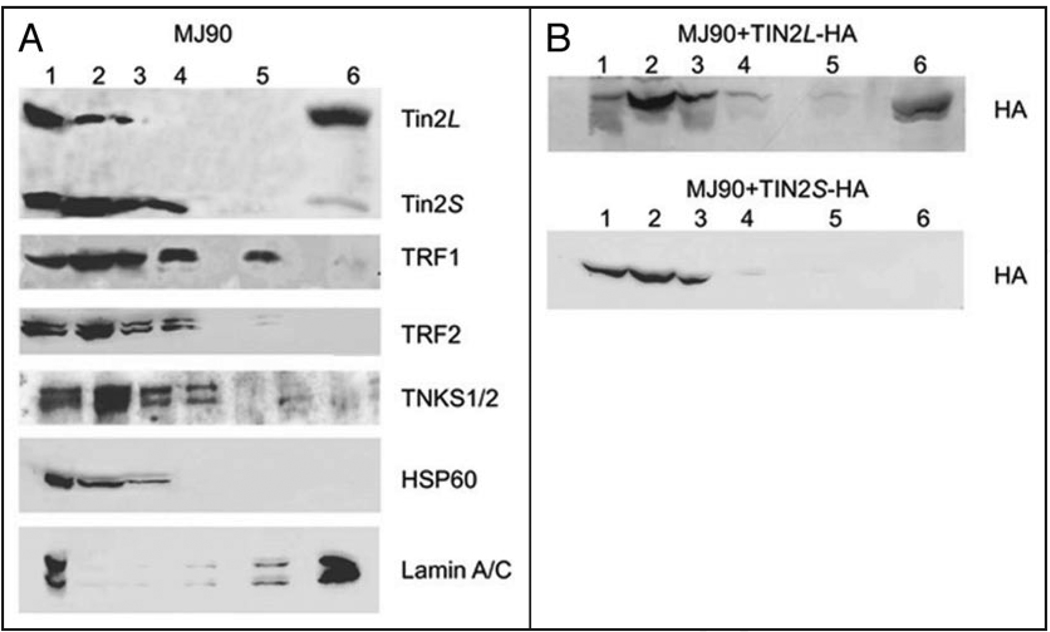
Figure 3.
Nuclear compartmentalization of hTIN2 isoforms. (A) Association of endogenous hTIN2 isoforms with nuclear fractions. Normal human fibroblasts (strain MJ90) were subjected to increasingly stringent extractions consisting of: 0.5% triton (lane 2), DNAse I digestion (lane 3), 0.25 M ammonium sulfate (lane 4) and 2 M NaCl (lane 5) extraction. The remaining pellet was solubilized in 2X Laemmli buffer (lane 6). Half the cell equivalents were solubilized directly in 2X Laemmli buffer (whole cell lysate) (lane 1) and used to determine the input. Equal cell equivalents were analyzed for each of the other fractions. Proteins were analyzed by western blotting using antibodies to detect the N-terminus of hTIN2, TRF1, TRF2, tankyrases (TNKS1/2), heat shock protein 60 (HSP60, a mitochondrial chaperone and cytoplasmic marker) and lamin A/C (insoluble nuclear matrix marker). (B) Solubilities of epitope-tagged hTIN2 isoforms. C-terminal epitope (HA)-tagged hTIN2 isoforms (hTIN2L-HA, hTIN2S-HA) were expressed in MJ90 cells, as described in the text and Materials and Methods. The cells were subjected to fractionation and analysis as described in A except that anti-HA antibodies were used for detection.