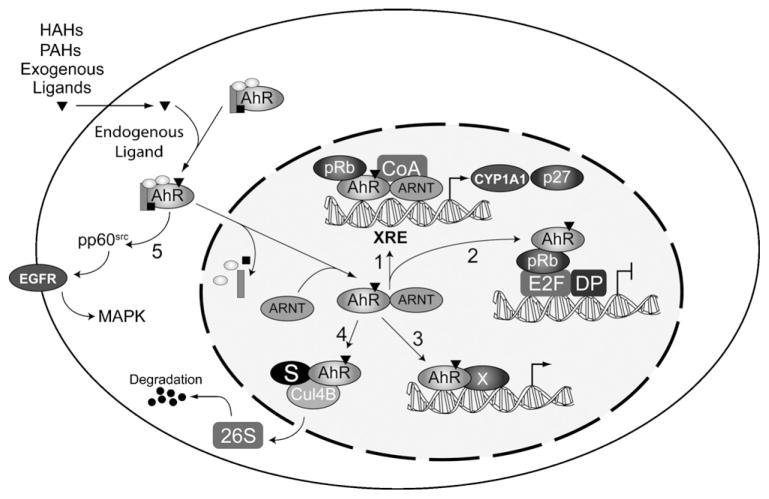
Fig. 2.
Multiple mechanisms involving aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-mediated cell signaling. The diagram depicts several mechanisms whereby AhR activity modifies cell signaling. Illustrated is the canonical xenobiotic response element (XRE)-bound AhR/ARNT complex with recruited coactivators (CoA; Scheme 1). AhR participation in transcriptional activation at non-XRE sites through indirect DNA-binding (Scheme 2), or direct DNA binding (Scheme 3). Additionally, two non-genomic modes of action involving AhR-mediated susbtrate (S) proteolysis involving cullin 4B (Scheme 4), and activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; Scheme 5) are presented.