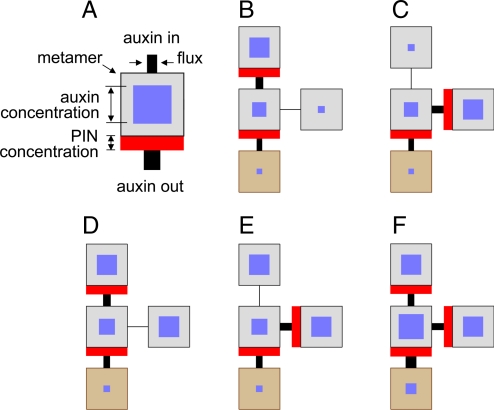
Fig. 1.
Pathways of auxin transport in a branching structure simulated using a canalization model (Eqs. 1 and 2). (A) Schematic representation of a metamer. Edge length of the blue square is proportional to auxin concentration; width of the red rectangle is proportional to the concentration of PIN proteins in the corresponding metamer face, and width of the lines entering or leaving a metamer is proportional to auxin flux. (B–F) Stable states in a branching structure consisting of 2 potential sources of auxin in the terminal and lateral positions, a branching node, and a sink in the proximal position. (B–C) Stable states of the system with a single auxin source in either terminal (B) or lateral (C) metamer. (D–F) Stable states of the system with 2 auxin sources. The terminal source has been established before (D), after (E), or near simultaneously (F) with the lateral source.