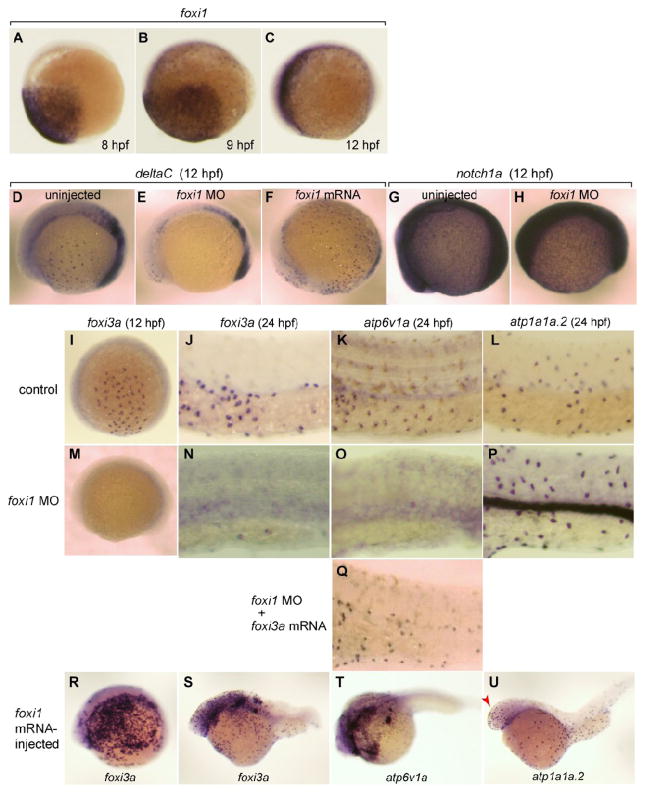
Fig. 3.
Broad expression of foxi1 in the presumptive ectoderm from 8 hpf and its regulatory role upstream of deltaC and foxi3a. (A-C) Whole mount in situ hybridization with foxi1 probe at 8 hpf (A), 9 hpf (B), and 12 hpf (C). (D-F) Whole mount in situ hybridization with deltaC probe at 12 hpf of uninjected wild-type control (D), foxi1 morphant (E), and foxi1 mRNA-injected embryos (F). (G, H) Whole mount in situ hybridization with notch1a probe at 12 hpf of uninjected (G) and foxi1 MO-injected (H) embryos. (I-U) Whole mount in situ hybridization with (i) foxi3a probe at 12 hpf (I, M, R) and 24 hpf (J, N, S), (ii) atp6v1a probe at 24 hpf (K, O, Q, T), and (iii) atp1a1a.2 probe at 24 hpf (L, P, U) of uninjected wild-type controls (I, J, K, L), foxi1 morphants (M, N, O, P), foxi1 morphant injected with foxi3a mRNA (Q), and foxi1 mRNA-injected embryos (R, S, T, U); for the controls of R-U, also see Figs. 2C, G, H. atp1a1a.2 and atp6v1a are marker genes for NaK-MRC and vH-MRC, respectively. Red arrow in panel U indicates foxi1-induced ectopic generation of NaK-MRC in the head region. Embryos are shown with their ventral side down and animal pole to the right.