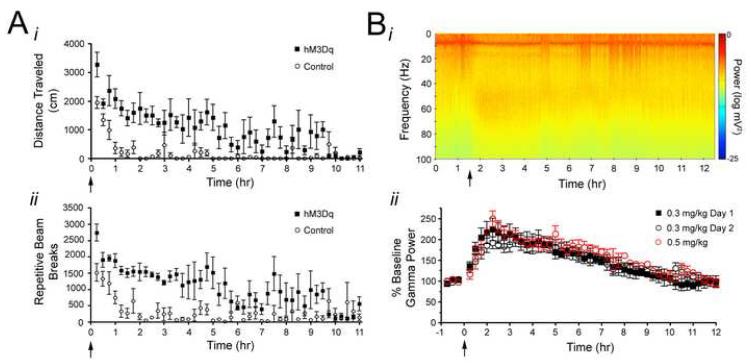
Figure 7. Behavioral and in vivo electrophysiological timecourse of CNO effects in hM3Dq animals.
A, Timecourse of CNO effects on locomotor activity, as measured by total distance traveled (i) and repeated beam breaks (ii), showing the latency to recovery of elevated locomotor activity following administration of 0.3 mg/kg CNO, which was administered at time 0 (n=4 littermate pairs). B, Timecourse of CNO effects on gamma power measured from the hippocampal LFP showing the latency to recovery of gamma power to baseline levels. Bi, Representative spectrogram of LFP from hM3Dq animal administered 0.3 mg/kg CNO at time 1.5 hr. ii, Population data demonstrating timecourse of acutely administered CNO on gamma power and gamma power response to two injections of CNO administered 24 hours apart from one another. The timecourse of onset and offset of CNO effects, as measured by changes in gamma power, was measured during an acute administration of either 0.3 mg/kg (closed black squares; n=3 hM3Dq animals) or 0.5 mg/kg (open red circle; n=2 hM3Dq animals) CNO to determine dose-dependence of onset and offset kinetics. Twenty four hours following the acute administration of 0.3 mg/kg CNO (Day 1; closed black squares), a second injection of 0.3 mg/kg CNO was administered to the same animals and gamma power response was monitored (Day 2; open black circles) for the purpose of assessing desensitization of the hM3Dq receptor.