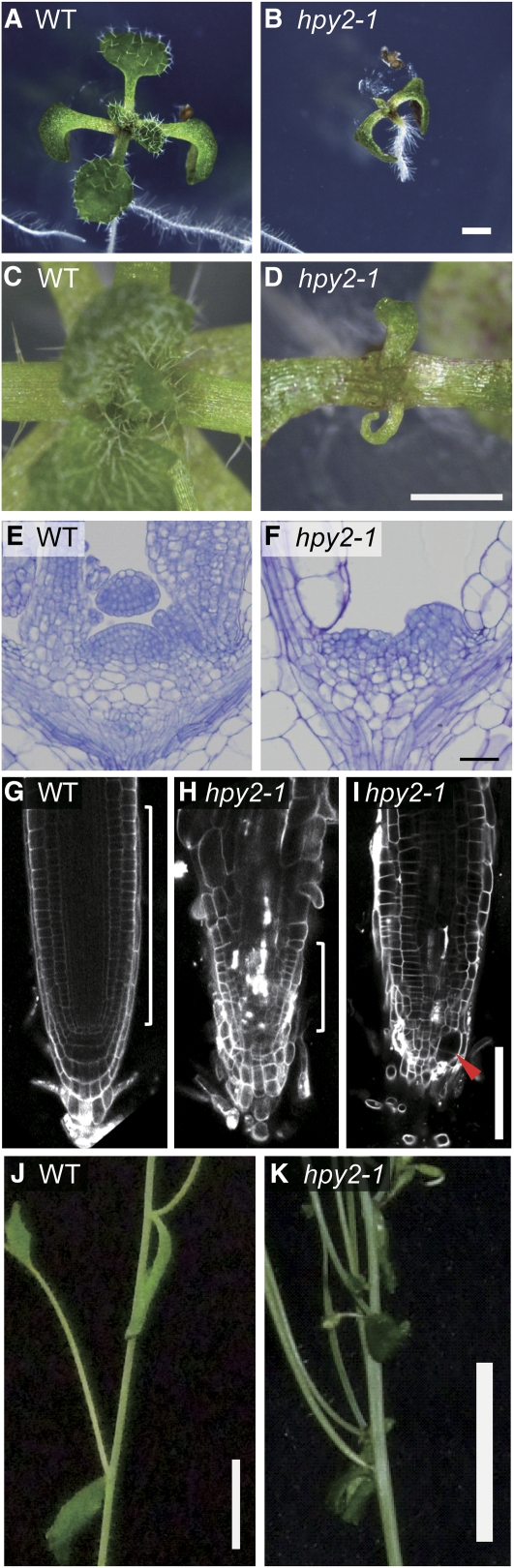
Figure 1.
hpy2 Mutants Are Defective in the Meristem Development.
(A) and (B) Ten-day-old seedlings of the wild type (A) and hpy2-1 (B).
(C) and (D) A close-up view of the shoot apices in 14-d-old wild-type (C) and hpy2-1 (D) seedlings.
(E) and (F) Histological sections of 6-d-old wild-type (E) and hpy2-1 (F) shoot apical meristems.
(G) to (I) Confocal microscopy of the PI-stained wild-type (G) and hpy2-1 ([H] and [I]) roots. White brackets in (G) and (H) mark the approximate position of root meristems. An optical section scanning closer to the root surface (I) reveals a swollen epidermal cell, indicated by an arrowhead, near the quiescent center.
(J) and (K) Fasciation and phyllotaxis defects of 30-d-old hpy2-1 plants (K) compared with the wild type (J).
Bars = 1 mm in (A) to (D), 20 μm in (E) and (F), 100 μm in (G) to (I), and 1 cm in (J) and (K).