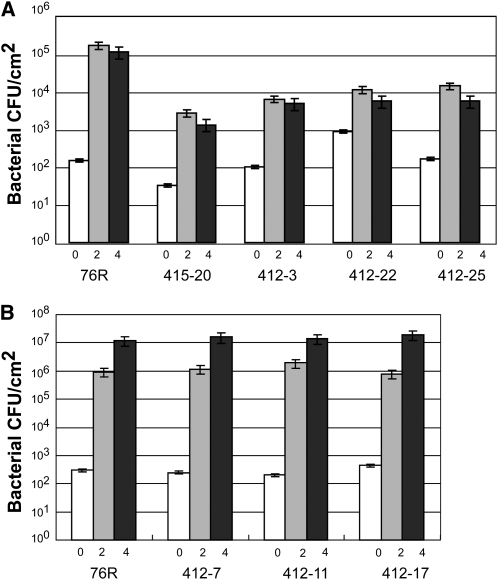
Figure 6.
Degradation of RIN4 Is Important for AvrPto-Dependent Inhibition of Bacterial Growth.
(A) Growth of P. syringae pv tomato T1 expressing avrPto was reduced in RIN4 RNAi-silenced T2 tomato plants. T2 plants derived from original (T1) transgenic plants 415 (one plant) and 412 (three plants) were inoculated by infiltrating the pathogen at 103 cfu/mL and assayed after 0 (white), 2 (gray), and 4 (black) d; error bars indicate the sd from three biological replications.
(B) Wild-type P. syringae pv tomato T1 exhibited normal levels of growth in RIN4 RNAi-silenced T2 plants. Three transgenic RNAi T2 plants derived from one RNAi-silenced T1 line (412) with reduced RIN4 expression relative to their isogenic wild-type tomato RG-76R were inoculated by infiltrating with pathogen at 103 cfu/mL and assayed 0, 2, and 4 d after infiltration. Error bars indicate the sd from three measurements.