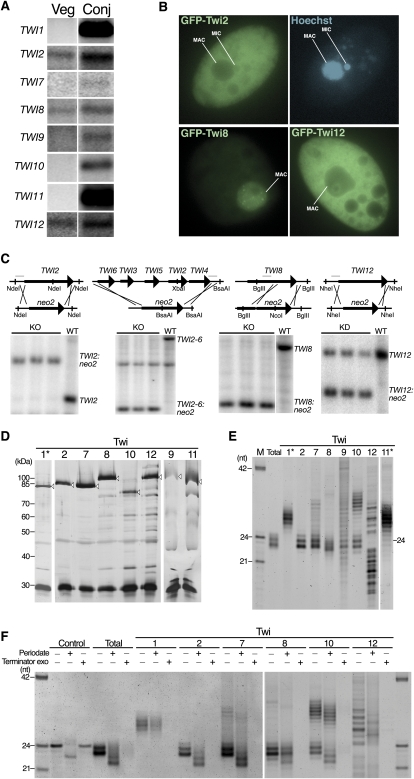
Figure 1.
Twi protein expression, localization, function, and bound sRNAs. (A) Northern blots to detect each TWI mRNA using total RNA isolated from cells in vegetative growth (Veg) or 9 h after initiating conjugation (Conj). (B) Imaging of live cells that expressed the indicated GFP-Twi fusion protein and were stained with the membrane-permeable dye Hoechst to visualize nuclei. (C) Southern blots to assess locus disruption by the neo2 selectable marker cassette. Restriction enzymes used for genomic DNA digestion are indicated along with the region used for probe (the thin gray line above the wild-type [WT] locus). (D) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing proteins obtained by affinity purification. Open arrowheads indicate the Twi protein after elution by TEV protease. The ∼30-kDa protein common to all lanes is recombinant TEV protease. Asterisk indicates purification from extract of conjugating cells harvested 6 h after conjugation initiation. (E) RNAs copurified with each Twi resolved by denaturing PAGE and stained with SYBR Gold. (M) Marker lane; (Total) gel-purified 23- to 24-nt sRNAs from strain CU522. Asterisk indicates purification from extract of conjugating cells harvested 4 or 10.5 h after conjugation initiation for Twi1 or Twi11, respectively. (F) End structure of sRNAs examined by β-elimination (Periodate) or 5′-monophosphate-dependent exonuclease treatment (Terminator exo). The control 24-nt RNA oligonucleotide has 2′- and 3′-hydroxyl groups but not a 5′ monophosphate.