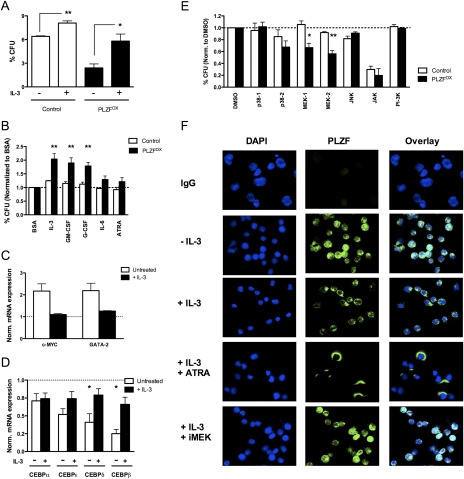
Figure 5.
Cytokines modulate the effects of PLZF on growth and differentiation. (A) Myeloid colony-forming capacity of CD34+ CD71− myeloid progenitors transduced with MPG (control) or MPG-PLZF (PLZFOX) viruses and seeded in methylcellulose ± IL-3. (B) Same as A, except progenitors were stimulated with the indicated cytokines for 24 h in SFM + BIT and seeded in methylcellulose. Data were normalized to BSA-treated samples (dashed line). (C) Expression of MYC and GATA-2 in control or PLZFOX CD34+ CD71− progenitors cultured for 4 d in serum-free media ± IL-3. Expression is normalized to cells infected with a control virus (dashed line). (D) Same as C for C/EBP transcription factors. Expression is normalized to cells infected with a control virus (dashed line). (*) P < 0.05. (E) Same as A, except progenitors were stimulated with IL-3 plus an indicated protein kinase inhibitor or DMSO vehicle for 24 h in SFM + BIT and seeded in methylcellulose. SB203580 inhibits p38-1, SB202190 inhibits p38-2, PD98059 inhibits MEK-1, U0126 inhibits MEK-2, SP600125 inhibits JNK, AG490 inhibits JAK, and LY294002 inhibits PI-3K. Data were normalized to DMSO-treated samples (dashed line). (F) Immunofluorescence staining of PLZF localization (green) in DAPI-stained nuclei or cytoplasm of nontransduced Lin− CD34+ CD71− progenitors cultured in SFM + BIT ± IL-3, ATRA, or PD98059 (iMEK) for 24 h. Magnification, 100×. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (*) P < 0.02; (**) P < 0.006.