Table 9.
Volume and ClogP parameters for carboxylesterase substrates
| Structure | Name | Vola | ClogPb |
|---|---|---|---|
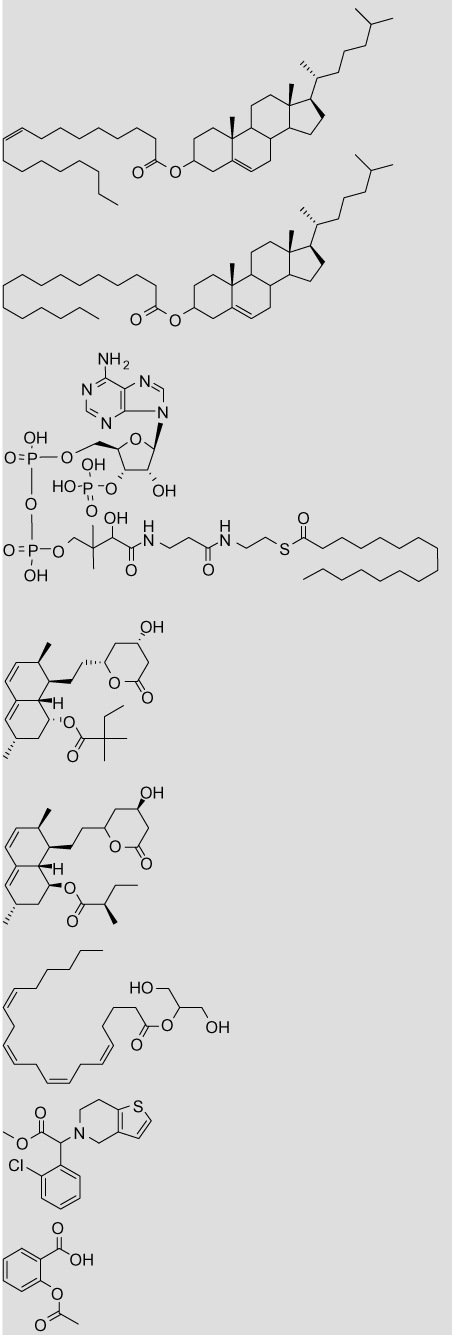 |
Cholesteryl oleate | 9.42 (11.81) | 18.45 |
| Cholesteryl palmitate | 9.81 (11.81) | 17.83 | |
| Palmityl-CoA | 9.11 (18.35) | 3.46 | |
| Simvastatin | 3.34 (9.27) | 4.68 (4.70) | |
| Lovastatin | 3.09 (9.43) | 4.26 (4.30) | |
| 2-Arachidonoyl glycerol | 10.49 (3.43) | 6.32 | |
| Clopidogrel | 7.21 (1.78) | 4.21 | |
| Aspirin | 1.42 (4.12) | 1.12 (1.02) | |
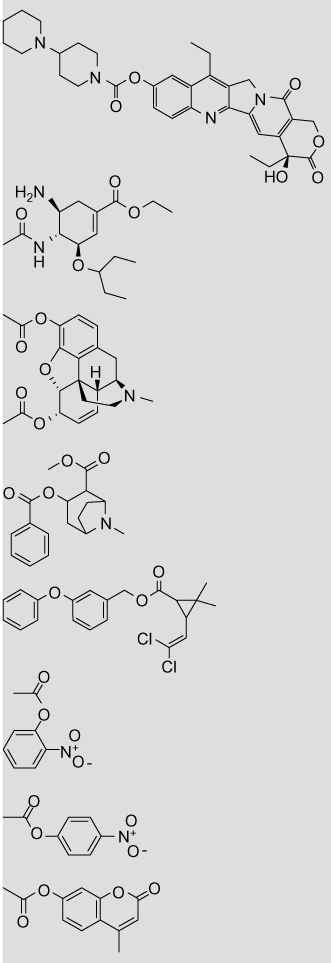 |
CPT-11 | 5.96 (10.22) | 2.72 |
| Oseltamivir | 7.58 (2.33) | 2.33 | |
| Heroin | 1.48 (8.54), 1.48 (8.68) | 1.58 (1.50) | |
| Cocaine | 7.22 (1.72), 3.13 (5.70) | 2.30 (2.57) | |
| Permethrin | 4.81 (6.10) | 6.50 (7.38) | |
| o-Nitrophenyl acetate | 1.48 (4.20) | 1.55 (1.50) | |
| p-Nitrophenyl acetate | 1.40 (4.07) | 1.50 (1.53) | |
| 4-Methyl umbelliferone acetate | 1.48 (5.28) | 1.90 (2.11) |
Volumes are given for the substrate hydrolysis products: the acid and the alcohol, with the alcohol value in parenthesis. The carbonyl group was excluded from all calculations. In cases where the substrate contains multiple ester moieties (cocaine and heroin), the volumes are given for the hydrolysis products of each ester. Volumes are not given for lactone hydrolysis in the statins (simvastatin and lovastatin) as the acid and alcohol moieties are still linked following hydrolysis.
The log P values were calculated with the program ClogP as described in Section 5. Values in parentheses are measured log P taken from literature sources.48
