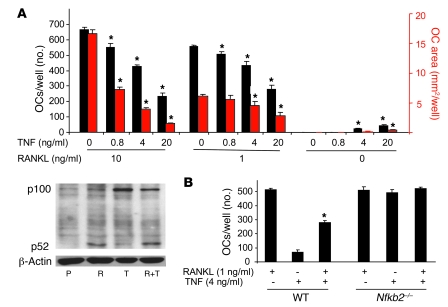
Figure 5. TNF-induced NF-κB p100 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis.
(A) WT mouse spleen cells were cultured with M-CSF for 3 days, and RANKL and/or TNF were added at the indicated doses for 2 more days to generate osteoclasts. Top: TNF dose-dependently inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, assessed by osteoclast number (black bars) and area (red bars) per well. Bottom: The protein levels of NF-κB p100 and p52 were analyzed with Western blot and assessed in whole-cell lysates extracted from RANKL-treated (10 ng/ml) and/or TNF-treated (20 ng/ml) WT mouse OCPs at 8 hours. (B) The inhibitory effect of TNF on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis was abolished in Nfkb2–/– OCPs (*P < 0.05 vs. RANKL treatment alone; 4 wells/group). The same experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results.