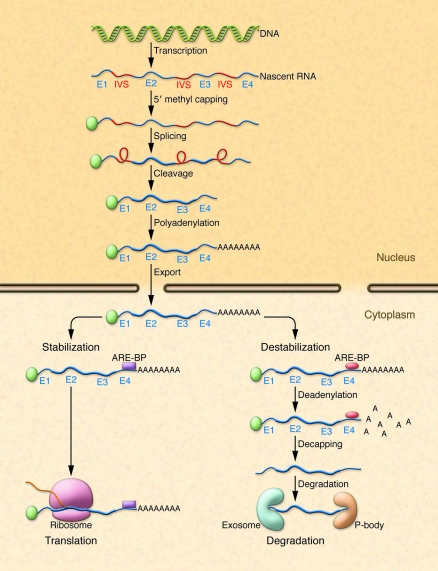
Figure 1. Cellular processing of RNA.
Following transcription, nascent RNA comprised of exons (E1–E4) and intervening sequences (IVS) is processed in the nucleus by 5′ methyl capping, splicing, cleavage, and polyadenylation. Processed RNA is exported from the nucleus and binds various structural elements and binding proteins. ARE-BPs (purple box and red oval) bind to AREs within the 3′ region of RNA and stabilize or destabilize mRNA. Stabilized RNA undergoes translation in ribosomes, whereas destabilized RNA undergoes deadenylation, decapping, and degradation in exosomes or P-bodies.