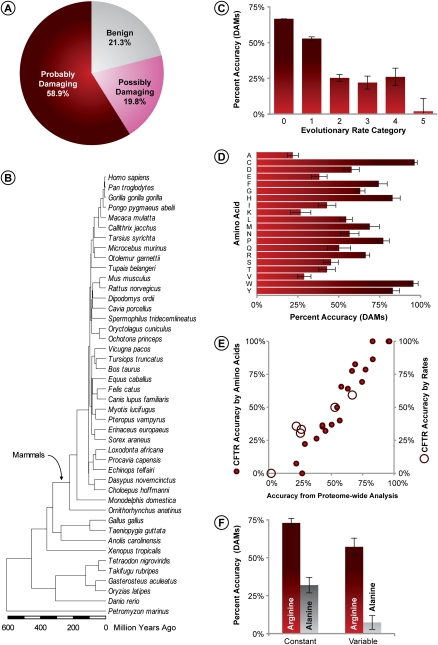
Figure 1.
Accuracy of PolyPhen diagnosis of 9460 DAMs. (A) Fraction of DAMs classified into benign, possibly-damaging, and probably-damaging categories. (B) Evolutionary timetree of 44 species used for estimating evolutionary rates. Relationship of evolutionary rates (C) and incident amino acids (D) with the correct diagnosis of DAMs (probably-damaging). Error bars, 95% confidence interval (two times the SE). (E) Correlation between the accuracy of DAM prediction from proteome-wide analysis, and one DAM-rich protein (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator [CFTR]). Solid and open circles show data points for incident amino acids (r = 0.97; P << 0.01) and evolutionary rates (r = 0.95; P << 0.01), respectively. (F) Two examples showing the dependence of the accuracy of DAM diagnosis for constant and variables sites for arginine (an easy-to-diagnose amino acid; red bars) and alanine (a difficult-to-diagnose amino acid; gray bars). Error bars, 95% confidence interval based on the binomial variance of the fraction of sites in the plotted categories.