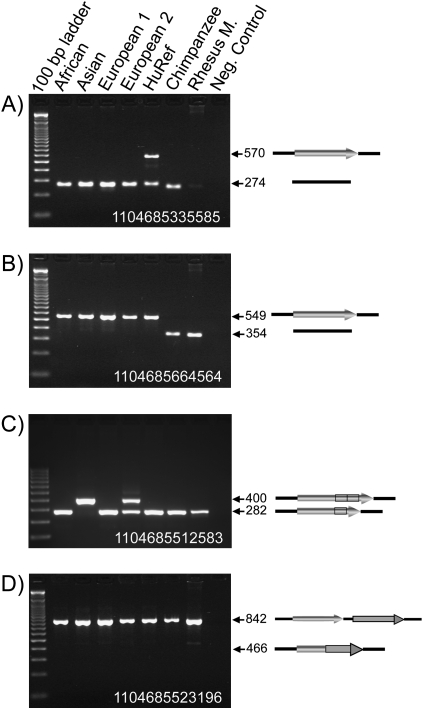
Figure 1.
PCR confirmation of the candidate MASVs. Four agarose gel chromatographs of the PCR products from a confirmation panel are shown. The DNA sample in each lane is labeled above the panel. (Arrows) Expected sizes (in bp) of the PCR amplicons. Diagrams representing the structure of each MASV allele are shown on the right of the panel. (Black line) Flanking DNA sequence, (filled arrows) mobile elements. (A) Locus 1104685335585, an Alu insertion that is heterozygous in the HuRef donor and absent in all other samples. The PCR products in the chimpanzee and the rhesus monkey are slightly smaller because of the smaller size of a (CA)n dinucleotide repeat in these genomes. (B) Locus 1104685664564, an Alu insertion that is present in all human samples tested but absent in the chimpanzee and rhesus macaque. (C) Locus 1104685512583, an L1 recombination-mediated indel. Because the HuRef sample is homozygous for the small size allele, as is the chimpanzee and rhesus macaque, this indel is likely to be caused by an insertion in the reference assembly. (Black box) The tandem duplication section inside the L1. (D) Locus 1104685523196, a false-positive Alu recombination-mediated deletion (ARMD) event where HuRef and all other samples are homozygous for the no-deletion allele.