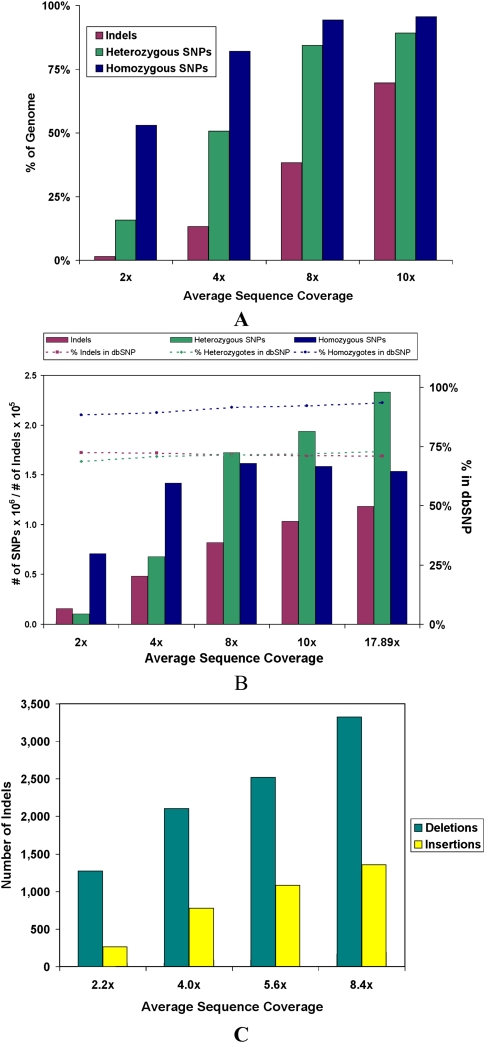
Figure 8.
Theoretical and actual detection of SNPs and indels at various levels of average sequence coverage. (A) The upper bound on the number of SNPs and intra-read indels that can be detected at various levels of coverage. This is calculated by assessing how much of the genome meets the coverage requirements for each type of variant, 2× coverage for homozygous SNPs, 4× coverage for heterozygous SNPs, and 6× coverage without considering the 3 bp on each end of the reads for intra-read indels. For small indels, two split reads are required to make a call, but due to the more restrictive manner of these calls, only about one in three reads (as found in simulations) can be used for this. (B) The actual number of SNPs and intra-read indels detected at various levels of average sequence coverage. (C) The number of insertions and deletions ≥200 bp detected between mate-paired reads at various average levels of sequence coverage.