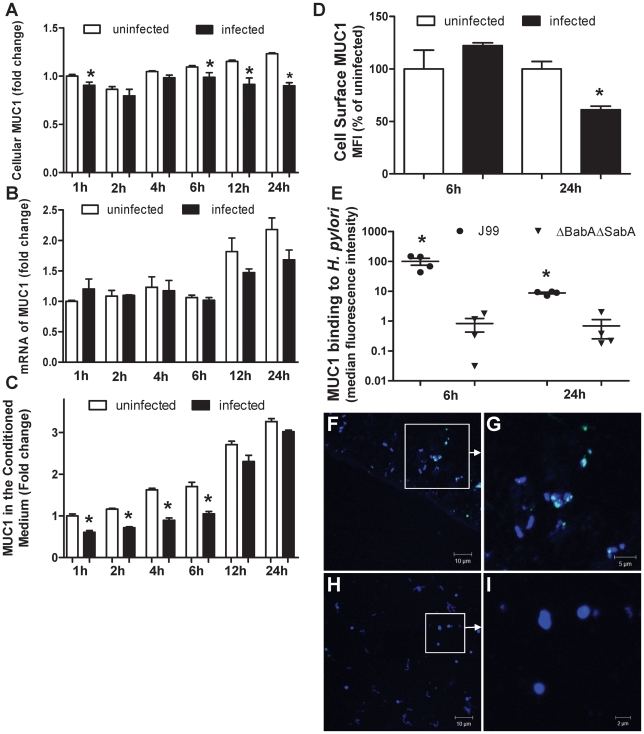
Figure 5. MUC1 is shed from the cell surface and binds H. pylori following co-culture in vitro.
MKN7 cells were uninfected or co-cultured with H. pylori J99 wild type for 1, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 h (MOI 10∶1) and total cellular MUC1 determined by BC2/BC3 double determinant ELISA as in Figure 3C (A), MUC1 mRNA concentrations relative to GAPDH were determined by qPCR (B), and concentrations of free MUC1 in conditioned medium determined by ELISA (C). In a further experiment after co-culture of MKN7 cells with H. pylori J99 wild type for 6 and 24 h cell surface MUC1 was assessed in MKN7 cells by flow cytometry as in Figure 4B (D). In a similar experiment both the J99 wild type (MOI 10∶1) and the J99ΔBabAΔSabA (20∶1) were co-cultured with MKN7 cells for 6 and 24 h and the presence of MUC1 on bacteria recovered from the conditioned media was determined by staining with the BC2 antibody or an isotype control followed by flow cytometry (E) and confocal microscopy (F–I). For flow cytometry the MFI of the isotype control was subtracted from the MFI of BC2-stained bacteria for each replicate culture. For confocal microscopy, H. pylori J99 wild type (F, G) or J99ΔBabAΔSabA (H, I) were stained with BC2 (FITC-conjugated secondary antibody, green), DNA (DAPI, blue); scale bars are shown (single scans and additional controls are shown in Figure S2). Scale bars are shown. Statistics: mean±SEM from 4 independent replicate co-cultures; Non-parametric test (Mann Whitney); vs non-infected at same time point (A, C, D) vs J99ΔBabASabA (E), * p<0.05.