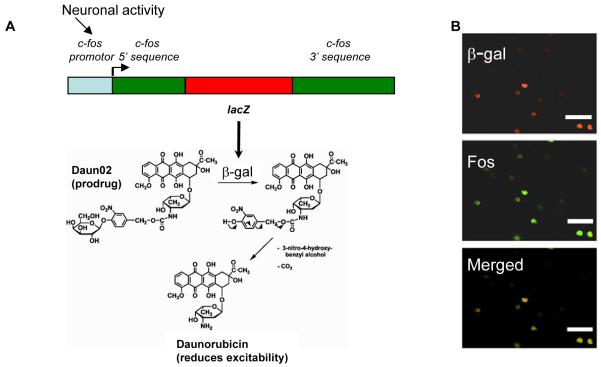
Figure 2.
Schematic mechanism for Daun02 inactivation in c-fos-lacZ rats. (A) The c-fos-lacZ transgene contains a c-fos promoter that drives expression of lacZ, which encodes the protein β-galactosidase (β-gal) (adapted from Schilling et al.39). β-galactosidase can catalyze the prodrug Daun02 into the daunorubicin (adapted from Farquhar et al.29), which reduces cellular excitability30. (B) Cocaine-induced neuronal activity induces β-galactosidase expression (red-labeled nuclei) and Fos-expressing (green-labeled nuclei) neurons in nucleus accumbens of sensitized c-fos-lacZ rats. Nuclei double-labeled for both β-galactosidase and Fos appear yellow to orange in the Merged image panel and indicate colocalization of β-galactosidase and Fos proteins. We performed quantitative analysis of cocaine-induced Fos and β-galactosidase co-localization in accumbens from three sensitized c-fos-lacZ rats. β-galactosidase was expressed in 100% of the Fos expressing neurons from all three rats and vice versa. Thus Daun02 can inactivate activated neurons that express both β-galactosidase and Fos. White bar indicates length of 50 micrometers.