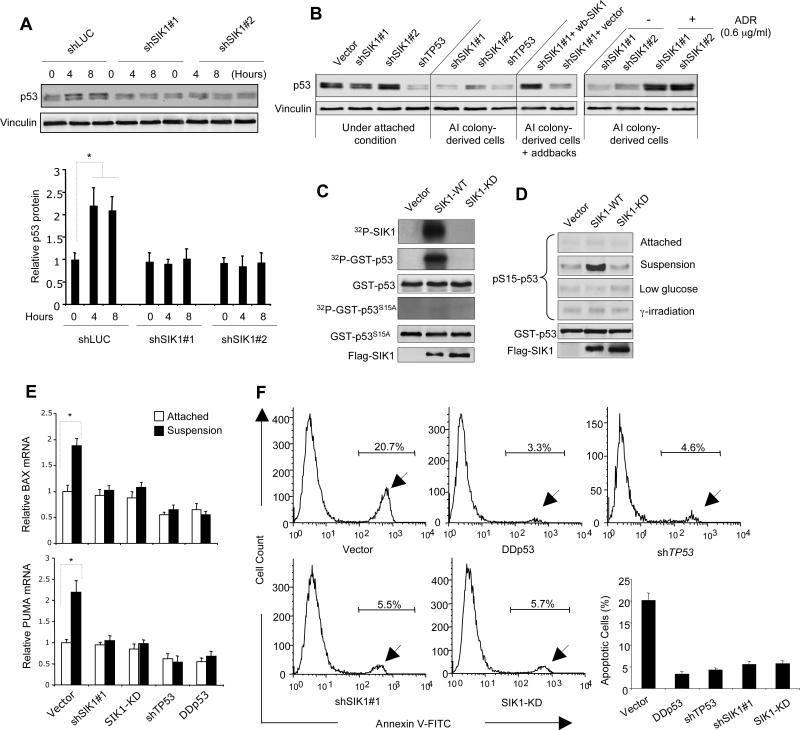
Fig. 2. SIK1 is required for p53-dependent anoikis.
(A) p53 protein abundance in HMECs expressing shSIK1s or shLuc cultured under attached or single cell suspension conditions for 4 or 8 hours, were examined by immunoblot analysis. Vinculin used as a loading control. Results are shown as the mean ± SD for 3 independent experiments. * p <0.01 (t-test) (B) Immunoblot analysis of p53 abundance in various tHMEC-P cell lines as indicated, as well as in colony-derived tHMEC-P-shSIK1 cells treated with adriamycin (ADR) (4.5 hr). wb-SIK1 (wobble SIK1), or vector, was expressed in AI colony-derived tHMEC-P-shSIK1#1 cells as indicated. (C) Kinase assays were used to detect auto-phosphorylation of SIK1 and phosphorylation of GST-p53 or GST-p53 S15A by Flag-tagged SIK1-WT or SIK1-KD immunoprecipitates. Radioactive signals were detected by phosphorimaging. (D) Phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 was determined by immunoblot following kinase assay using Flag-tagged SIK1 immunocomplexes (WT or KD) from U2OS cells subjected to different conditions. (E) PUMA and BAX expression in tHMEC-P cells expressing shSIK1#1, SIK1-KD, shTP53, or p53DD cultured attached or in suspension for 16 hours was determined by real-time RT-PCR. Mean ± SD for 3 independent experiments are shown. * p <0.01 (t-test) (F) Inactivation of SIK1 renders cells resistant to anoikis. tHMEC-P cells were cultured in suspension for 2 days, and the percentage of apoptotic cells expressing various cDNAs or shRNAs was determined by Annexin-V staining. Mean ± SD for 3 independent experiments are shown. * p <0.001 (t-test).