Figure 1. Inducible, Multisite Serine Phosphorylation in EPRS Linker Domain.
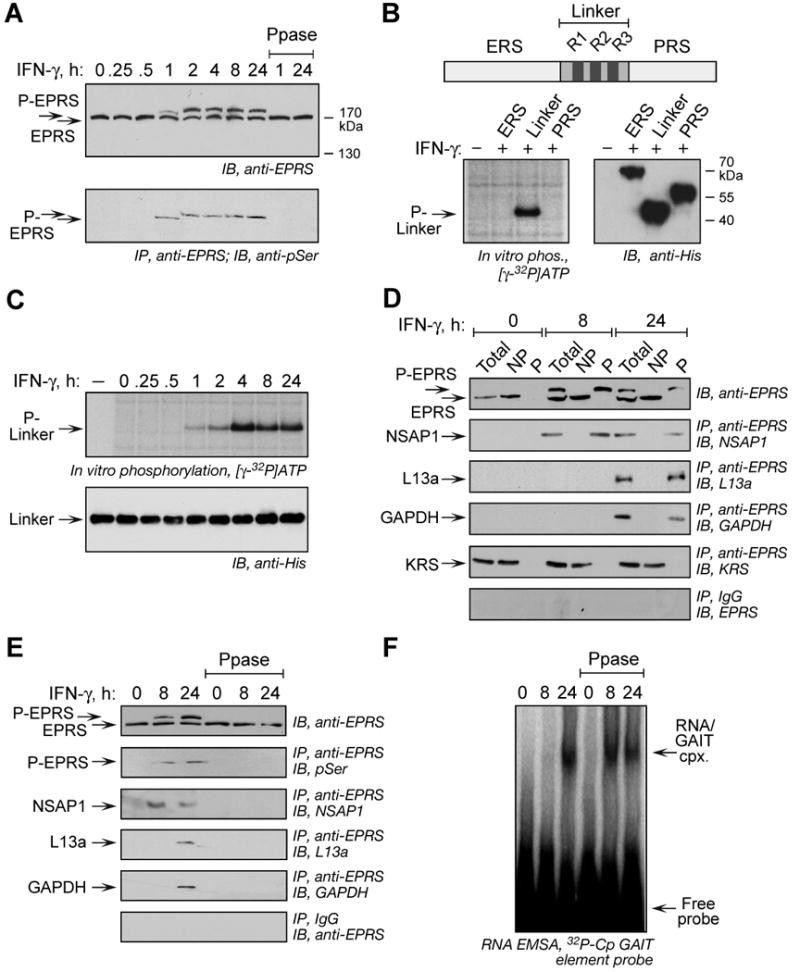
(A) Multisite EPRS phosphorylation. Phosphorylated EPRS (P-EPRS) in lysates from IFN-γ-treated U937 cells was resolved by SDS-PAGE (4.5% polyacrylamide) and detected by immunoblot with anti-EPRS antibody. Two samples were incubated with shrimp alkaline phosphatase (PPase) before immunoblot analysis. The same lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-EPRS antibody and probed with anti-pSer antibody.
(B) The non-catalytic EPRS linker domain is phosphorylated. Schematic of major human EPRS domains. In vitro phosphorylation of His-tagged EPRS domains by lysates of 24-h, IFN-γ-treated U937 cells. All domains detected by immunoblot with anti-His antibody.
(C) Lysates from IFN-γ treated cells were used to in vitro phosphorylate recombinant, His-tagged EPRS linker. Linker was detected by immunoblot with anti-His antibody.
(D) EPRS phosphorylation is required for release from MSC and interaction with GAIT proteins. Lysates from IFN-γ treated U937 cells were applied to phosphoprotein affinity column to isolate P-EPRS and unmodified EPRS. Total, non-phosphorylated (NP), and phosphorylated (P) fractions were assessed by immunoblot with anti-EPRS antibody. The same fractions were immunoprecipitated with anti-EPRS and detected with antibodies against GAIT constituent proteins and the MSC constituent KRS. As a control, fractions were immunoprecipitated with rabbit IgG and immunoblotted with anti-EPRS.
(E) Dephosphorylation of EPRS disrupts the pre-GAIT and GAIT complexes. Lysates from IFN-γ-treated U937 cells were incubated with shrimp alkaline phosphatase and dephosphorylation detected with anti-EPRS antibody, and by immunoprecipitation with anti-EPRS and immunoblot with anti-phosphoSer. Precipitates were probed with antibodies against all GAIT proteins.
(F) EPRS phosphorylation is not required for binding to GAIT element. EPRS binding to GAIT element was determined by RNA EMSA using 32P-labeled Cp GAIT element RNA probe in control and phosphatase-treated lysates of IFN-γ-activated cells.
