Figure 4. EPRS Phosphorylation is Required for Release from MSC.
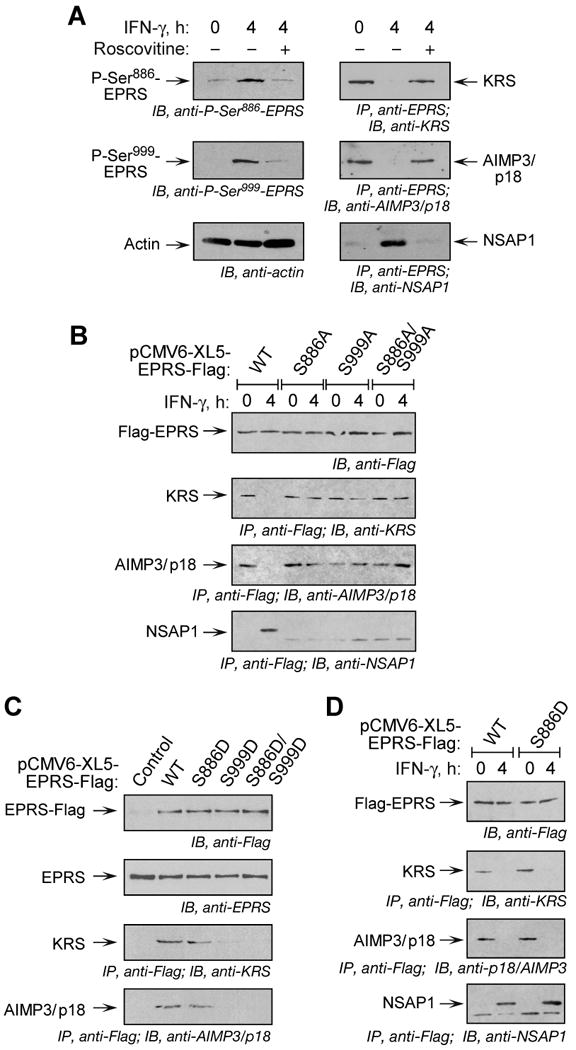
(A) Inhibition of phosphorylation blocks EPRS release from MSC. U937 cells were treated with IFN-γ and roscovitine or DSMO as in Fig. 3D. Lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies indicated. Same lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-EPRS antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies against MSC components, KRS and AIMP3/p18, or against the pre-GAIT complex protein, NSAP1.
(B) Both Ser phosphorylation events are required for EPRS release from MSC. Flag-tagged, full-length, wild-type (WT) or phosphorylation-defective (Ser-to-Ala, S-A) EPRS mutants were cloned into pCMV6-XL5 vector and expressed in U937 cells by transient transfection. After 18 h, cycloheximide (50 μg/ml, 30 min) was added to block new synthesis, and then incubated with IFN-γ for 4 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies indicated.
(C) Incorporation of EPRS phospho-mimetics into MSC. Flag-tagged, full-length, WT and phospho-mimetic (Ser-to-Asp, S-D) mutant EPRS was expressed in U937 cells by transient transfection as in (B) and measured by immunoblot with anti-Flag antibody. Endogenous EPRS was detected by anti-EPRS antibody. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies indicated.
(D) Release of S886D phospho-mimetic establishes dual-site phosphorylation-dependent release of EPRS from MSC. Cells expressing Flag-tagged, full-length EPRS were incubated with IFN-γ for 4 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies indicated.
