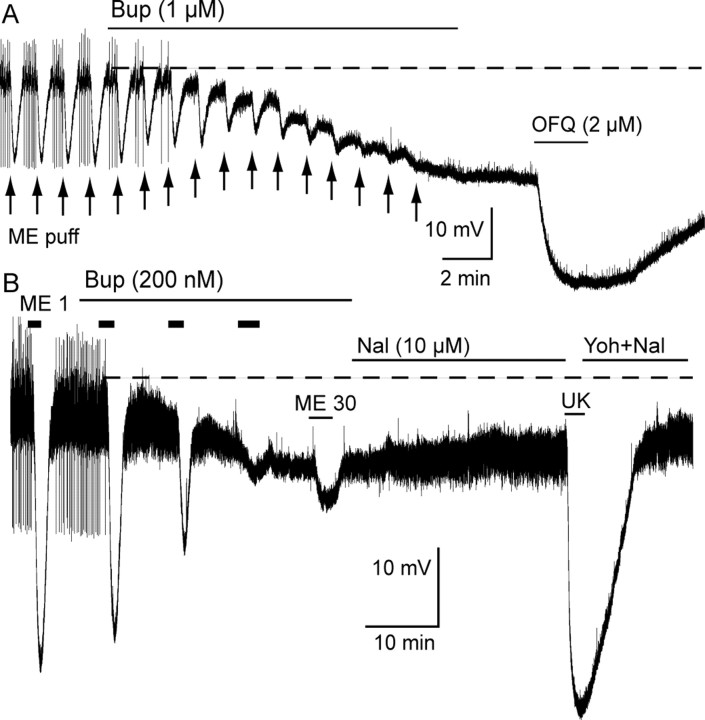
Figure 1.
Buprenorphine hyperpolarized LC neurons and blocked the ME-induced hyperpolarization. Voltage recording made with intracellular electrodes. A, Buprenorphine (Bup; 1 μm) was applied for 15 min and caused a sustained hyperpolarization. Pressure ejection of ME (ME puff, arrows) caused a transient reproducible inhibition in spontaneous firing and hyperpolarization that was blocked by the application of buprenorphine. Application of orphanin FQ/nociception (OFQ) resulted in an additional hyperpolarization. B, ME (1 μm, 2 min) caused an inhibition of spontaneous firing and a hyperpolarization of ∼25 mV. Buprenorphine (200 nm) caused a hyperpolarization over a period of 25 min. The hyperpolarization induced by ME (1 μm) was decreased by buprenorphine, and, after 25 min, application of ME (30 μm) caused only a small hyperpolarization. Naloxone (Nal; 10 μm for 25 min) had little effect on the membrane potential. UK14304 (UK, 3 μm) caused a hyperpolarization of ∼35 mV. Yoh, Yohimbine.