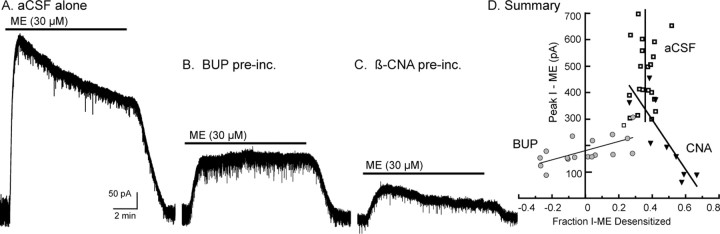
Figure 2.
Buprenorphine limits ME-induced desensitization. Voltage-clamp recordings made with whole-cell electrodes. A, A control experiment using an untreated slice. ME (30 μm) caused a large outward current that declined during the 10 min application period. B, An experiment taken from a slice that was preincubated with buprenorphine (Bup; 5 nm, 1 h). ME (30 μm) caused a small outward current that did not desensitize during the 10 min application. C, An experiment using a slice that was preincubated with β-CNA (20 nm, 1 h). ME (30 μm) caused a small outward current that desensitized during the 10 min application period. D, Summary of results, plotting the peak amplitude of the current induced by ME (30 μm) against the amount of desensitization (the change in current from the peak to the end of the 10 min application divided by the peak current). The open boxes (vertical line at 35%) indicate experiments done in control slices (A). The amount of desensitization was independent of the initial amplitude of current induced by ME. The gray circles (positive sloping line) are experiments done after buprenorphine (B). In this case, when the current induced by ME was larger, the amount of desensitization was greater. When the ME currents were smaller than 150 pA, the desensitization was eliminated. Filled triangles (negative sloping line) are experiments done after β-CNA (C). In this case, as the current induced by ME decreased, the amount of desensitization was increased.