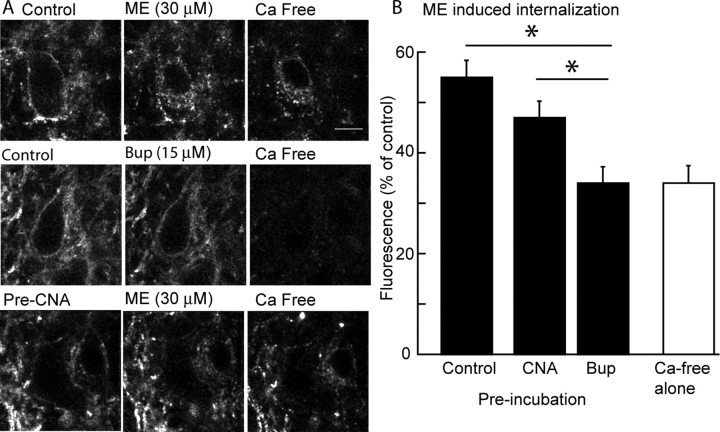
Figure 5.
Buprenorphine does not cause receptor internalization and blocked the internalization induced by ME. A, Images of cells in three experiments. Left, Images taken at the beginning of the experiment after incubating slices with M1 anti-Flag antibody without drugs (top 2 images) or β-CNA (10 nm, 1 h; bottom image). The top three images are a control experiment demonstrating the internalization of receptor evoked by ME (30 μm, 15 min). The fluorescence image on the right is only internalized receptors after treatment of the slice with a calcium-free solution to strip antibody bound to extracellular surface. Middle images show that buprenorphine (15 μm) did not induce any internalization. The bottom images show that treatment of slices with a low concentration of β-CNA reduced but did not abolish the ME-induced receptor internalization. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Summarized results from several experiments showing the amount of internalization (fluorescence as a percentage of the control) induced by ME in control, after treatment of slices with β-CNA (10 nm, 1 h) or buprenorphine (Bup; 5 nm, 1 h). The open bar is the background fluorescence measured after treatment of the slices with calcium-free solution without application of any drug. *p < 0.05.