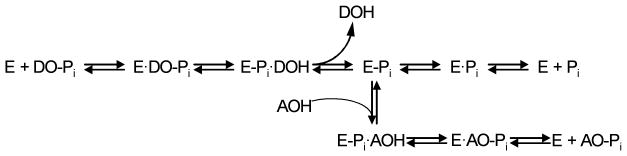
Figure 2.
The catalytic mechanism of the alkaline phosphatase reaction.12 The initial alkaline phosphatase (E) catalyzed reaction consists of a substrate (DO-Pi) binding step, phosphate-moiety transfer to Ser-93 (in the TNAP sequence of its active site) and product alcohol (DOH) release. In the second step of the reaction, phosphate is released through hydrolysis of the covalent intermediate (E-Pi) and the non-covalent complex (E·Pi) of the inorganic phosphate in the active site. In the presence of nitrogen-containing alcohol molecules (AOH), such as the buffer diethanolamine (DEA), phosphate is also released via a transphosphorylation reaction.