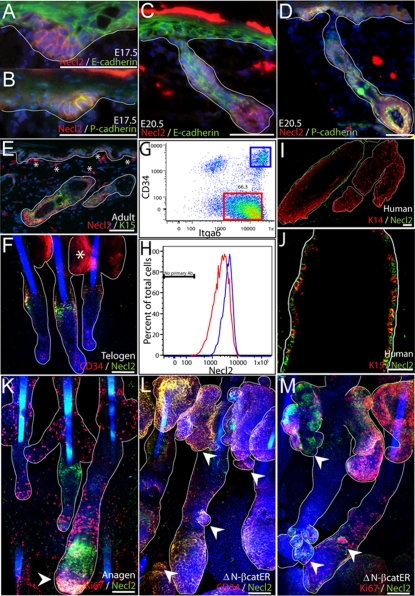
Fig. 1.
Necl2 expression in developing and adult epidermis. (A-D) E17.5 (A,B) or E20.5 mouse skin (C,D) was stained for Necl2 (red) and E-cadherin (green, A,C) or P-cadherin (green, B,D) with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). (E,F) Adult mouse back skin section (E) and tail epidermal whole-mount (F) stained with antibodies against Necl2 (red, E; green, F) and keratin-15 (green, E) or CD34 (red, F) with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Note staining of sebaceous glands (asterisk, F) is nonspecific. (G,H) Flow cytometric analysis of Necl2 expression (H) in adult integrin-α6 (Itga6)-positive basal cells (red box, G) and CD34- and Itga6-positive bulge cells (blue box, G). (I,J) Adult human hair follicles stained for Necl2 (green) and keratin-14 (red, I) or keratin-15 (red, J). (K) Necl2 (green) and Ki67 (red) immunostaining of adult mouse anagen follicles (tail epidermal whole mount) with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Arrowhead indicates Necl2 expression in hair follicle bulb. (L,M) Adult tail whole mounts of K14ΔNβ-cateninER epidermis treated with 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen for 2 weeks and stained for Necl2 (green) and CD34 (red, L) or Ki67 (red, M) with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Arrowheads indicate ectopic hair follicles arising from sebaceous glands and existing follicles. White lines (A-F, I-M) indicate position of basement membrane or delineate hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Scale bars: 100 μm in A-F,I-M.