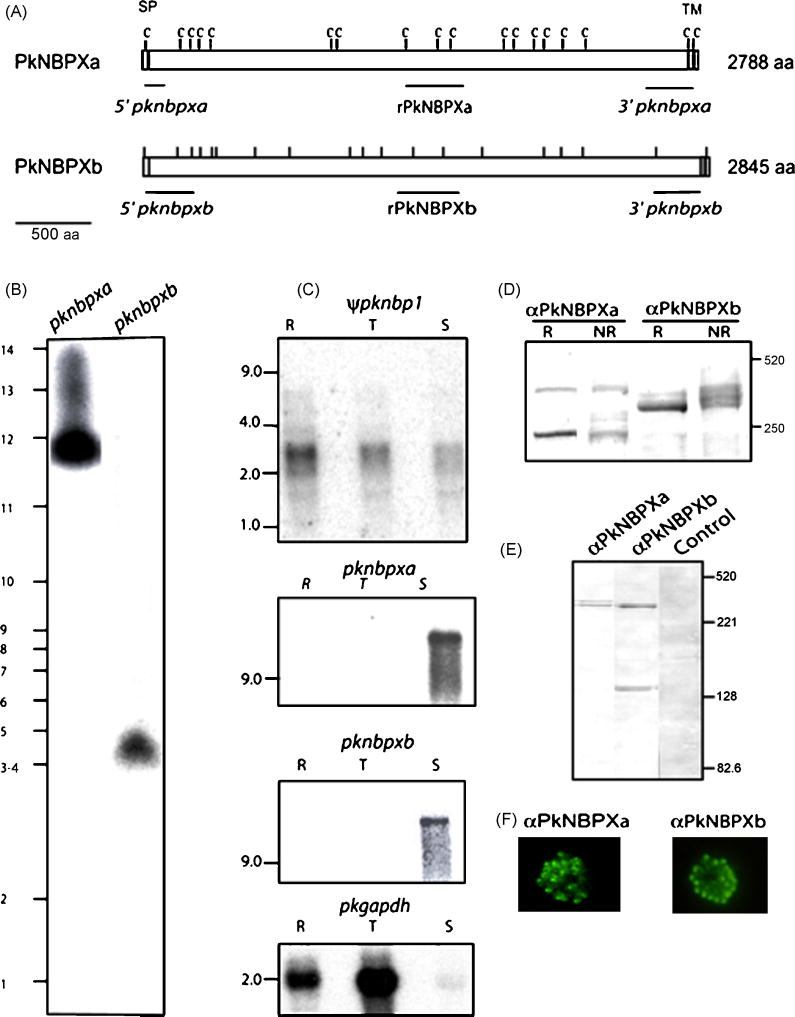
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic of the P. knowlesi PkNBPXa and PkNBPXb RBL proteins with cysteine residues (tick marks), positions of the signal peptides (SP), a large extracellular domain and a transmembrane domain (TM) shown. Probes used for chromosomal Southern and Northern blot hybridizations are indicated in italics and the fragments expressed as recombinant proteins are indicated in bold letters. (B) The pknbpxa and pknbpxb genes were localized in chromosomes 3–4 and 12, respectively, by PFGE using the pknbpxa and pknbpxb probes. (C) Total RNA from ring stages (R), late trophozoites and early schizonts (T) and late schizonts (S) was hybridized with radiolabeled probes representing the 5′ end of the ψpknbp1 gene, and the central regions of pknbpxa and pknbpxb genes using high stringency conditions. Apparent ψpknbp1 partial transcripts (~3 kb) were detected in ring, trophozoite and schizont stages, compared to pknbpxa and pknbpxb transcripts of >9kb, which were detected only in the matured schizonts. The Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene was used as positive control (pkgapdh). PkNBPXa and PkNBPXb were detected by western blot in P. knowlesi-schizont-infected erythrocytes solubilized with SDS-PAGE sample buffer with (R, reduced) or without (NR, non-reduced) 2-mercaptoethanol (D), and in supernatant collected after schizont rupture (E). The NBPXa1 antisera recognized specific bands of ~300 kDa and 250 kDa, and the NBPXb1 antisera recognized bands of ~300k Da and 140 kDa (D and E). PkNBPXa and PkNBPXb native proteins were identified by IFA using rabbit antisera PkNBPXa1 or PkNBPXb1, respectively. The robust single dot pattern typical for the PvRBPs at the apical pole was observed in segmented schizont-stage parasites; pre-immune sera were used as negative control (F).