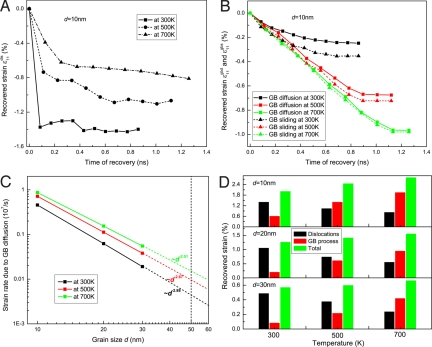
Fig. 5.
Contributions of GB- and dislocation-mediated deformation mechanisms to total plastic strain recovery. (A) Recovered strain due to dislocation mechanisms as a function of time in the d = 10 nm sample. (B) Recovered strains due to GB sliding and GB diffusion as a function of time in the d = 10 nm sample. (C) Grain size dependence of strain rate due to GB diffusion. The values of strain rate corresponding to grain size of d = 50 nm are estimated by a linear extrapolation. (D) Fractional strains due to GB and dislocation processes at different grain sizes and temperatures.