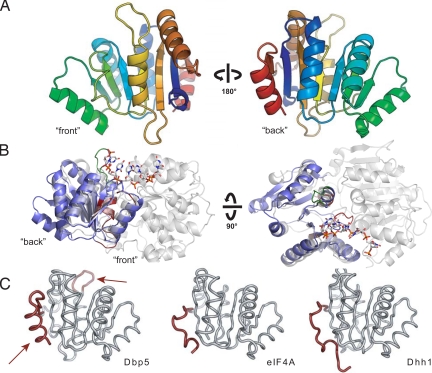
Fig. 1.
Structure of the Dbp5 CTD. (A) “Front” and “back” views of the secondary structure features of Dbp5. (B) Position of the Dbp5 CTD in the context of a full-length DExD/H-box ATPase. Side and top views of Dbp5 CTD (blue) superposed on the Vasa helicase from Drosophila (gray) (29) show the orientation of the CTD in the context of an active RNA helicase assembly. The front of the domain faces the active site cleft and contains the conserved DExD/H sequence motifs (shown in red), whereas the back is distal to the interdomain interaction surface. The Dbp5-specific six amino-acid insertion is highlighted in green. (C) Comparison of Dbp5 CTD with the CTDs of eIF4A (30) and Dhh1 (31). Dbp5 CTD possesses two elements shown in red: an extended loop element after strand β5 (Top, arrow) and a conserved α-helix (Bottom, arrow) at its C-terminus that are not present in other structurally characterized DExD/H-box proteins.